
© Harry Campbell & Richard Brown
School of Economics
The University of Queensland
BENEFIT-COST ANALYSIS
BENEFIT-COST ANALYSIS
Financial and Economic
Financial and Economic
Appraisal using Spreadsheets
Appraisal using Spreadsheets
Ch 13: Economic Impact Analysis

What is the difference between Net Present Value
and Economic Impact?
Keynes gives the example of land, labour and capital used in two
alternative ways:
1. To dig a hole in the ground;
2. To build a hospital.
The two projects have the same economic impact, in terms of
generating income for factors of production and inducing additional
expenditures, but the hospital has a higher net present value than the
hole in the ground.
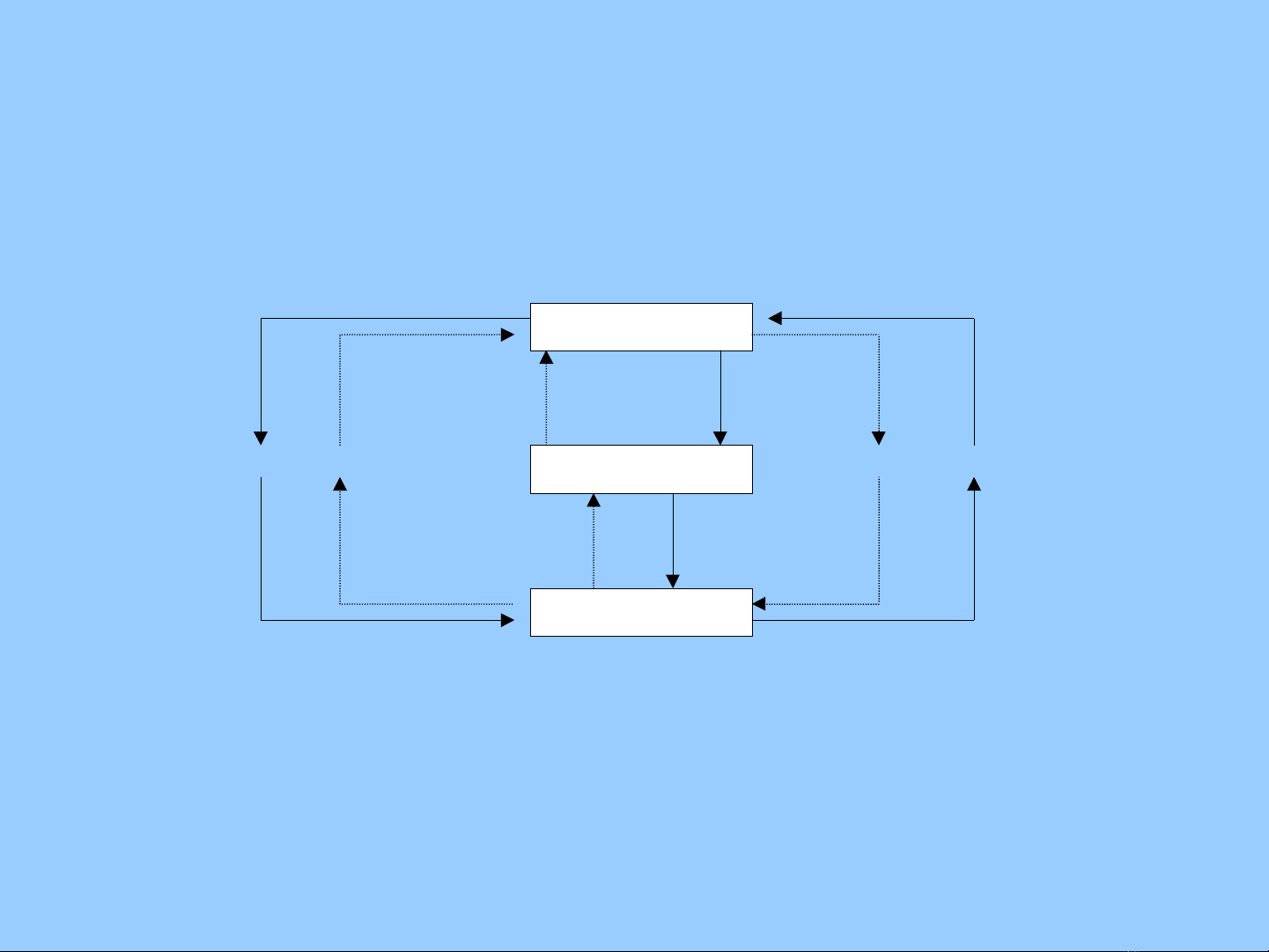
Figure 13.1 The Circular Flow of Income
$ GOODS FACTORS $
GOVERNMENT
HOUSEHOLDS
FIRMS
The Circular Flow of National Income

The National Income Multiplier
Consider three models which can be used to derive the national
income multiplier:
1. A closed economy, no taxes;
2. A closed economy, with exogenous taxes;
3. An open economy, with endogenous taxes.
Symbols:
Y = national income; C = consumption expenditure;
S = Savings; I = investment expenditure;
T = tax revenues; G = government expenditure;
X = value of exports; M = value of imports

Model 1: Closed economy, no taxes
Y = C + I + G
C = A* + bY,
where A* is autonomous consumption expenditure, and
investment and government expenditure are exogenous.
Substitute to get:
Y = A* + bY + I* + G*
where “ * ” indicates a variable which is exogenous to the model
(i.e. is assumed to be constant).
Solve to get:
Y = (1/(1-b))(A* + I* +G*),
where (1/(1-b) is the national income multiplier.
Now dY = (1/(1-b) dG*










![Phân Tích Dự Án Dưới Rủi Ro: [Thêm Mô Tả Chi Tiết Để Tối Ưu SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2013/20130221/muaxuan102/135x160/6881361431722.jpg)















