
Chapter 5 1
K THU T NÂNG –V N CHUY NỸ Ậ Ậ Ể
CHƯƠNG 5
CƠ C U NÂNGẤ
(MOTIVE POWER OF HOISTING
MACHINERY)
Chapter 5 2
1. D N Đ NG MÁY TR CẪ Ộ Ụ
( motive power of hoisting machinery)
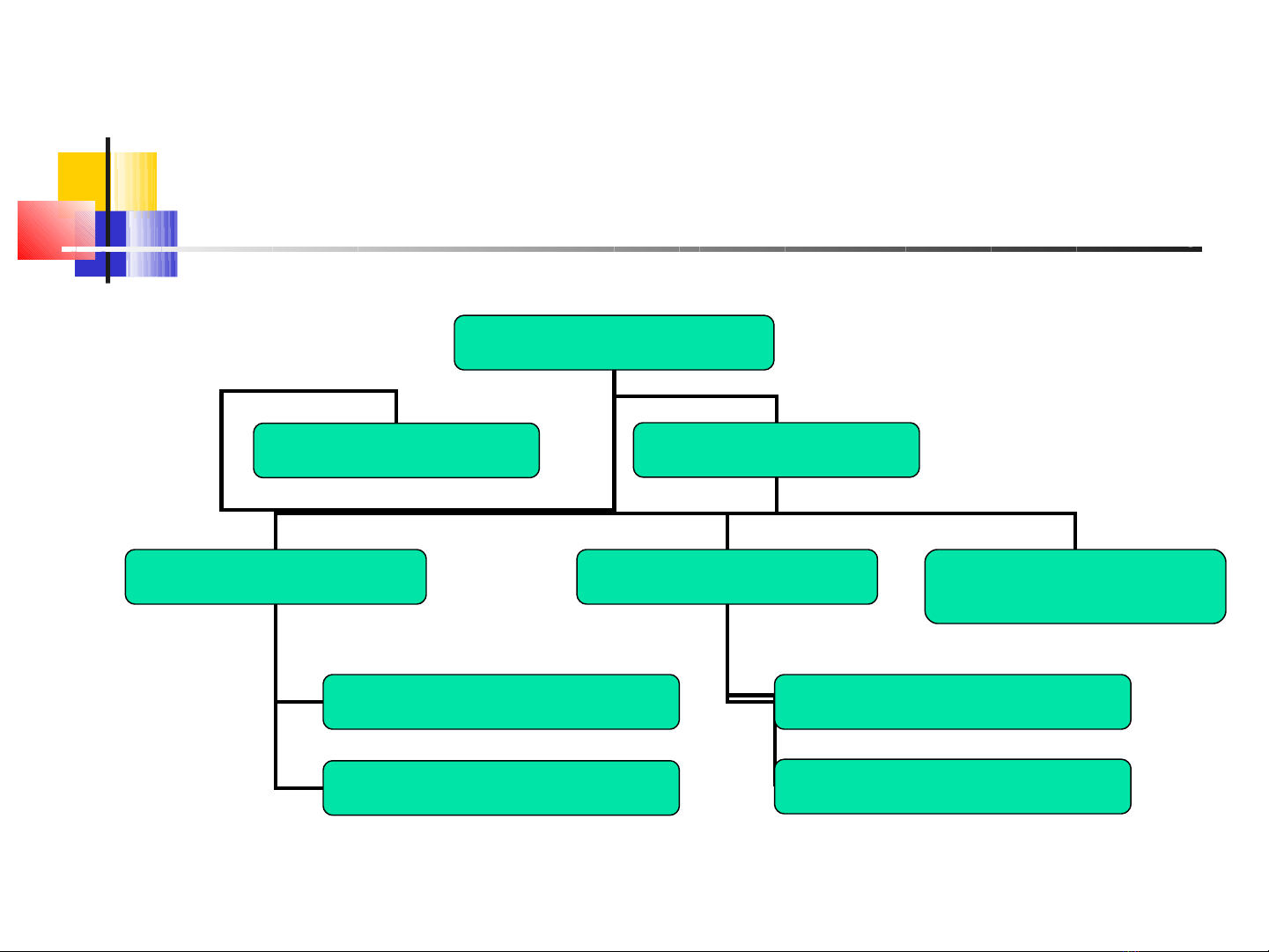
Daãn ñoäng maùy truïc
Daãn ñoäng tay Daãn ñoäng maùy
Ñoäng cô ñieän Ñoäng cô ñoát trong Ñoäng cô thuûy löïc
Ñoäng cô khí neùn
Ñoäng cô moät chieàu
Ñoäng cô xoay chieàu
Ñoäng cô xaêng
Ñoäng cô diezen
Chapter 5 3
1. D N Đ NG MÁY TR C(tt)Ẫ Ộ Ụ
a) Đ ng cộ ơ đi n (The electric drive)ệ
Đ ng cộ ơ đi n 1 chi u (a): kích ệ ề
thích song song , n i ti p, h n ố ế ỗ
h p ợ
=> có kh nảăng đi u khi n ề ể
cao nhưng giá thành l n.ớ
(D.c motor are provided in three
standard types by the way they
are excited. These are the series
motor, shunt motor, and
compound motor)

Chapter 5 4
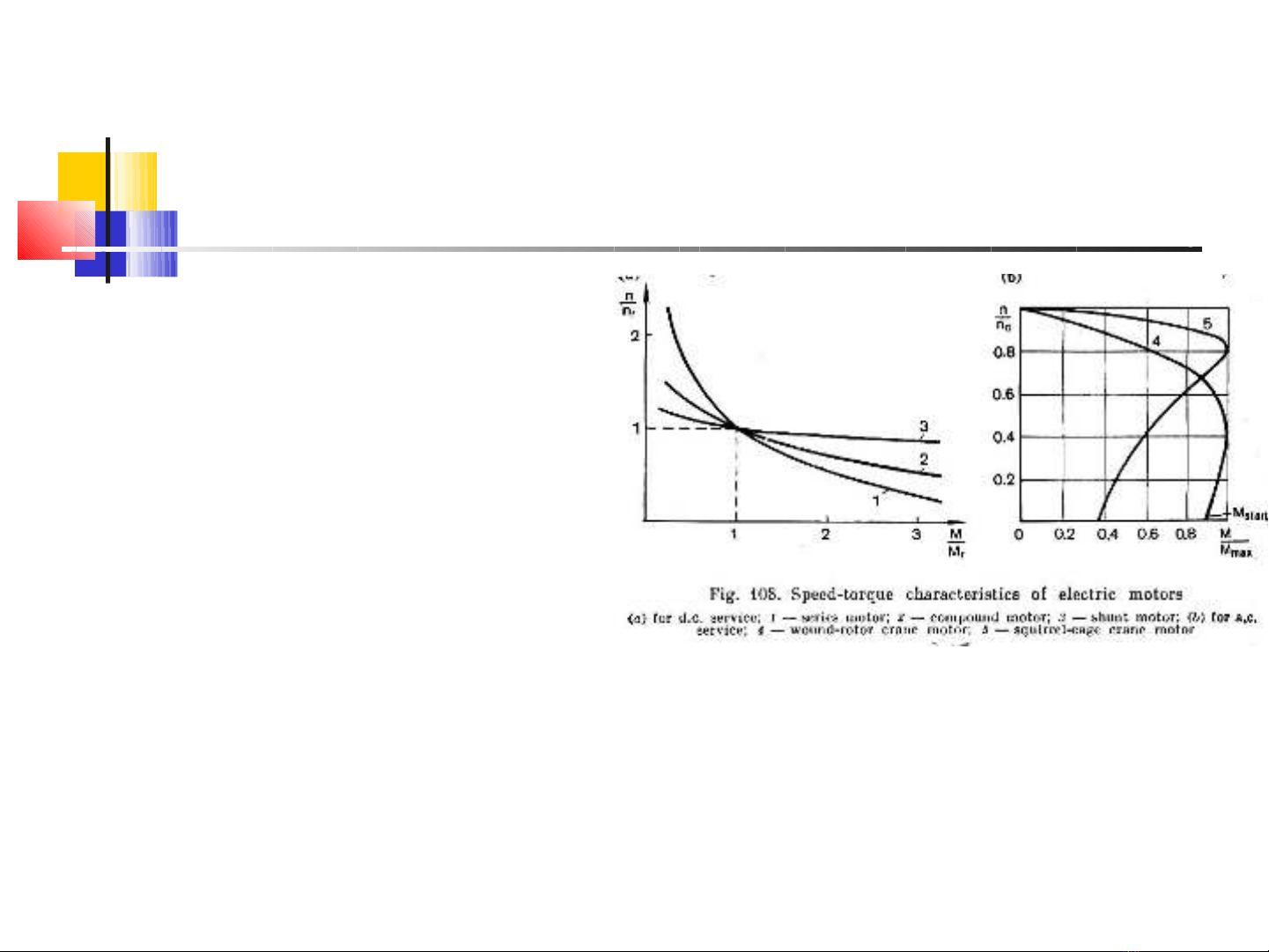
Đ ng cộ ơ đi n xoay chi u (b): có kích thệ ề ư c g n, giá thành th p.ớ ọ ấ
L ng sócồ: m máy b ng n i sao, tam giác (r hở ằ ố ẻ ơn) (5).
Dây cu nố: m máy b ng ở ằ đi n tr phu (4)ï.ệ ở
(Distinction is made between squirrel-cage (5) and wound- rotor a.c.
(4) crane motor
-The fact that the speed- torque characteristic of the squirrel- case
motor is flat as that as of the shunt motor in handling rated loads
indicated that the speed changes but little with load. Squirrel- case
motors are the most reliable and inexpensive a.c prime mover.
-Wound motors are somewhat heavier and larger than squirrel- case
ones. At the same time, the losses of energy in windings during the
transient periods are smaller in the former than in later)
1. D N Đ NG MÁY TR C (tt)Ẫ Ộ Ụ
a) Đ ng cộ ơ đi n (The electric drive)ệ

Chapter 5 5
1. D N Đ NG MÁY TR C (tt) Ẫ Ộ Ụ
b) Đ ng cộ ơ đ t trong ố
( internal combustion device)
Đ ng cộ ơ xăng (petrol engine)
Đ ng cộ ơ điezen. (diezel engine)
=> Máy có ph m vi ho t ạ ạ đ ng l n.ộ ớ

![Đề cương bài giảng Nguyên lý động cơ [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250715/kimphuong1001/135x160/75891752564030.jpg)





![Bài giảng Nguyên lý máy: Chương 5 - Đại học Xây dựng Hà Nội [FULL]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250423/echdada123/135x160/2892319_5577.jpg)

![Bài tập tối ưu trong gia công cắt gọt [kèm lời giải chi tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251129/dinhd8055/135x160/26351764558606.jpg)














