
Specific membrane binding of the carboxypeptidase Y
inhibitor I
C
, a phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein
family member
Joji Mima*, Hiroaki Fukada, Mitsuru Nagayama and Mitsuyoshi Ueda
Division of Applied Life Sciences, Graduate School of Agriculture, Kyoto University, Japan
Endogenous protein inhibitors of lysosomal ⁄vacuolar
proteases are found in the cytoplasm of various euk-
aryotic organisms, from microorganisms to mammals.
Lysosomal ⁄vacuolar proteases are responsible for the
majority of intracellular protein degradation and turn-
over, but no definitive information on the physio-
logical roles of cytoplasmic inhibitors has been
reported. I
C
, carboxypeptidase Y (CPY) inhibitor, was
isolated as an endogenous cytoplasmic inhibitor of
vacuolar CPY in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[1–3]. Recent biochemical and mutational studies of I
C
[4–8] and the crystal structure of the complex of I
C
with CPY (I
C
–CPY) [8,9] have provided information
on the nature of the inhibition. The N-terminal acetyl
group of I
C
is essential for inhibitory function, and
the inhibitor forms an equimolecular complex with
the cognate protease through dual binding sites, an
N-terminal inhibitory reactive site and a secondary
Keywords
I
C
; membrane binding; PEBP;
phosphatidylserine; phosphoinositide
Correspondence
J. Mima, Division of Applied Life Sciences,
Graduate School of Agriculture,
Kyoto University, Kitashirakawa, Sakyo-ku,
Kyoto 606-8502, Japan
Fax: +81 75 753 6112
Tel: +81 75 753 6125
E-mail: mima@kais.kyoto-u.ac.jp
*Present address
Department of Biochemistry, Dartmouth
Medical School, Hanover, NH, USA
(Received 7 July 2006, revised 4 October
2006, accepted 9 October 2006)
doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05530.x
I
C
, an endogenous cytoplasmic inhibitor of vacuolar carboxypeptidase Y in
the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is classified as a member of the phos-
phatidylethanolamine-binding protein family. The binding of I
C
to phos-
pholipid membranes was first analyzed using a liposome-binding assay and
by surface plasmon resonance measurements, which revealed that the affin-
ity of this inhibitor was not for phosphatidylethanolamine but for anionic
phospholipids, such as phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylinositol 3-phos-
phate, phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate, and phosphatidylinositol
3,4,5-trisphosphate, with K
D
values below 100 nm. The liposome-binding
assay and surface plasmon resonance analyses of I
C
, when complexed with
carboxypeptidase Y, and the mutant forms of I
C
further suggest that the
N-terminal segment (Met1–His18) in its carboxypeptidase Y-binding sites
is involved in the specific and efficient binding to anionic phospholipid
membranes. The binding of I
C
to cellular membranes was subsequently
analyzed by fluorescence microscopy of yeast cells producing the green
fluorescent protein-tagged I
C
, suggesting that I
C
is specifically targeted to
vacuolar membranes rather than cytoplasmic membranes, during the sta-
tionary growth phase. The present findings provide novel insights into the
membrane-targeting and biological functions of I
C
and phosphatidyletha-
nolamine-binding proteins.
Abbreviations
CPY, carboxypeptidase Y; FM4-64, N-(3-triethylammoniumpropyl)-4-(p-diethylaminophenylhexatrienyl) pyridinium dibromide; GFP, green
fluorescent protein; I
C
, carboxypeptidase Y inhibitor; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PEBP, phosphatidyl-
ethanolamine-binding protein; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PS, phosphatidylserine; PtdIns, phosphatidylinositol; PtdIns(3)P, phosphatidylinositol
3-phosphate; PtdIns(4)P, phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate; PtdIns(5)P, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate; PtdIns(3,4)P
2
, phosphatidylinositol
3,4-bisphosphate; PtdIns(3,5)P
2
, phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate; PtdIns(4,5)P
2
, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
,
phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate; SPR, surface plasmon resonance.
5374 FEBS Journal 273 (2006) 5374–5383 ª2006 The Authors Journal compilation ª2006 FEBS
CPY-binding site [6–8]. In addition to its function as a
protease inhibitor, it has also been shown that I
C
is
identical to Tfs1p [4], a multicopy suppressor of the
cdc25-1 mutant [10], and that it inhibits and interacts
with the yeast Ras GTPase-activating protein, Ira2p [11].
The amino acid sequence of I
C
shows similarity to
sequences of, not other known protease inhibitors, but
rather members of the phosphatidylethanolamine-bind-
ing protein (PEBP) family, which is highly conserved
among many organisms, such as mammals, plants,
worms, and bacteria [4,12]. A variety of molecular
functions of PEBPs in mammals have been reported to
date, and include the association with phospholipids
and membranes [13–16], the inhibition of Raf1 kinase
[17,18], thrombin [19], and G-protein-coupled receptor
kinase 2 [20], and the N-terminal fragment serving as
the hippocampal cholinergic neurostimulating peptide
[21,22]. In plants, two homologs of PEBP from Arabid-
opsis thaliana, FT and TFL1, were identified as floral
regulators that may interact with FD, a bZIP tran-
scription factor [23–26]. The crystal structures of
PEBPs from several organisms, including the structure
of I
C
–CPY, have also been determined [8,27–32]. These
structures demonstrate that PEBPs contain two repre-
sentative structural features, a central b-sheet fold and
a conserved anion-binding site that may recognize
phosphate groups of phospholipids and ⁄or phosphor-
ylated residues in potential binding partners [8,27–32],
whereas the molecular mechanisms for the putative
functions of PEBPs, except for CPY inhibition by I
C
[8], remain obscure.
In the present study, we report on a detailed study
of the membrane-binding mode of I
C
, a PEBP family
member. A liposome-binding assay and surface plas-
mon resonance (SPR) analysis indicate that I
C
specific-
ally binds to membranes containing anionic
phospholipids, rather than phosphatidylethanolamine
(PE). A cellular localization analysis of I
C
by fluores-
cence microscopy, using the green fluorescent protein
(GFP), subsequently revealed the localization of this
inhibitor at vacuolar membranes.
Results
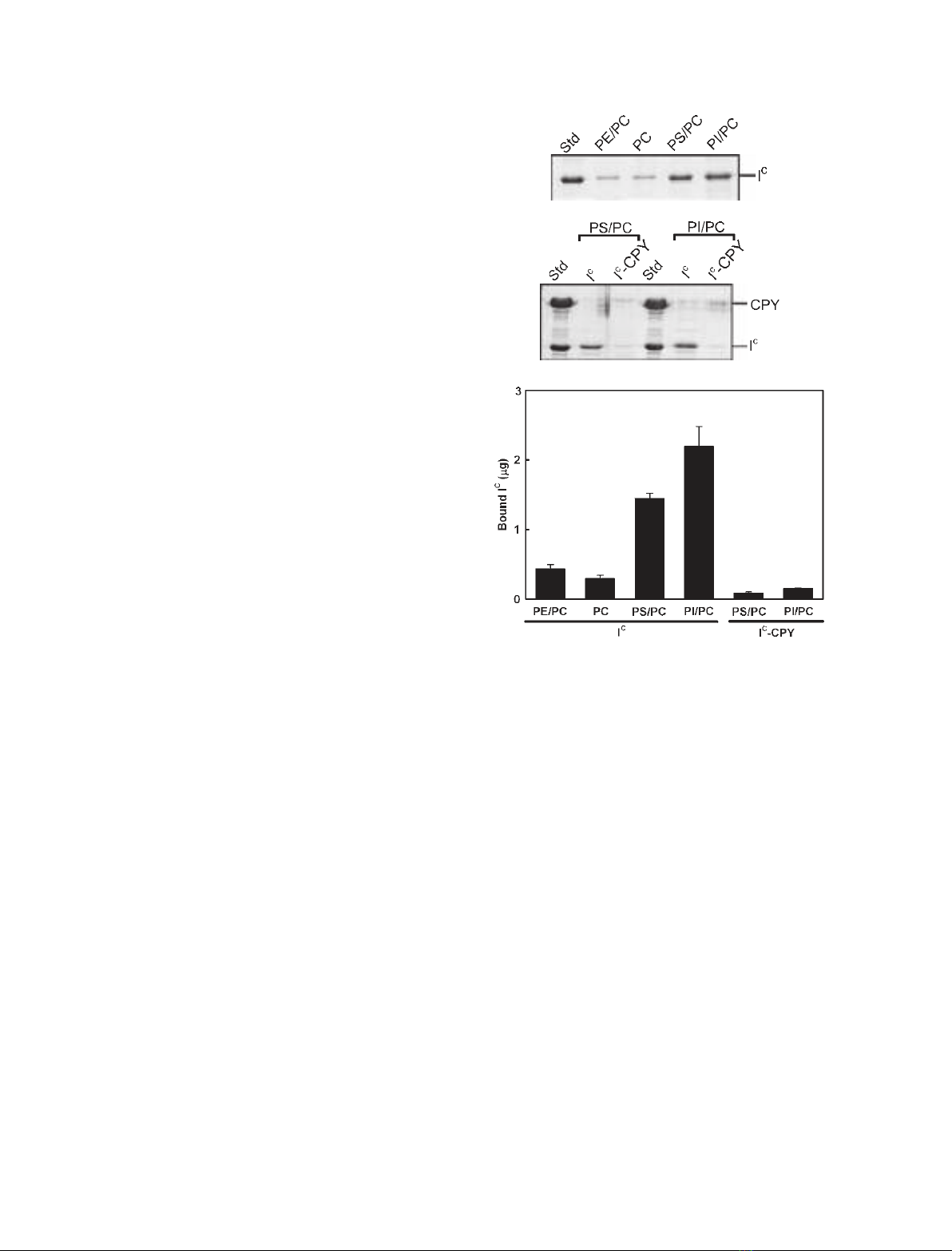
Membrane-binding properties of I
C
In an attempt to detect and characterize the membrane
binding of I
C
, a member of the PEBP family, we first
performed a liposome-binding assay of this inhibitor
for the phosphatidylcholine (PC)-based liposomes
(Fig. 1). As shown in Fig. 1A,C, SDS ⁄PAGE analysis
of the precipitates, which were mixtures of I
C
and lipo-
somes, indicated that considerably larger amounts of
this inhibitor were sedimented with phosphatidylserine
(PS) ⁄PC and phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) ⁄PC than
with PC and PE ⁄PC. This experiment provided an esti-
mate of the affinity of binding of I
C
to phospholipid
membranes, and demonstrated that I
C
has an affinity
for anionic phospholipids such as PS and PtdIns,
rather than for zwitterionic phospholipids, such as PE
and PC. In addition to free I
C
,I
C
–CPY was subjected
to the binding assay with PS ⁄PC and PtdIns ⁄PC lipo-
somes. As shown in Fig. 1B,C, neither I
C
nor CPY in
I
C
–CPY was sedimented with these liposomes, indica-
ting that the affinity of I
C
for anionic phospholipids
disappeared upon complex formation with CPY.
A
B
C
Fig. 1. Liposome-binding assay for I
C
and I
C
–CPY. I
C
(A) or I
C
–CPY
(B), the final concentration of which was 2 lM, was added to PC-
based liposomes (0.5 mgÆmL
)1
of PE ⁄PC, PC, PS ⁄PC, and
PtdIns ⁄PC) in 20 mMHepes (pH 7.2) containing 0.15 MNaCl, and
the suspension was incubated at 30 C for 1 h. After centrifugation
of the samples, proteins bound to liposomes were analyzed by
SDS ⁄PAGE of the resulting pellets. (C) The amounts of I
C
in the
pellets. The amounts of I
C
were quantitated with the UN-SCAN-IT gel
program (Silk Scientific Corporation, Orem, UT) using the band of
purified I
C
(2 lg) as a standard control. Error bars indicate SD from
two or more determinations.
J. Mima et al.Membrane binding of I
C
FEBS Journal 273 (2006) 5374–5383 ª2006 The Authors Journal compilation ª2006 FEBS 5375
Therefore, these results suggest that the binding inter-
face for CPY in the I
C
molecule is involved in its spe-
cific binding to anionic phospholipid membranes.
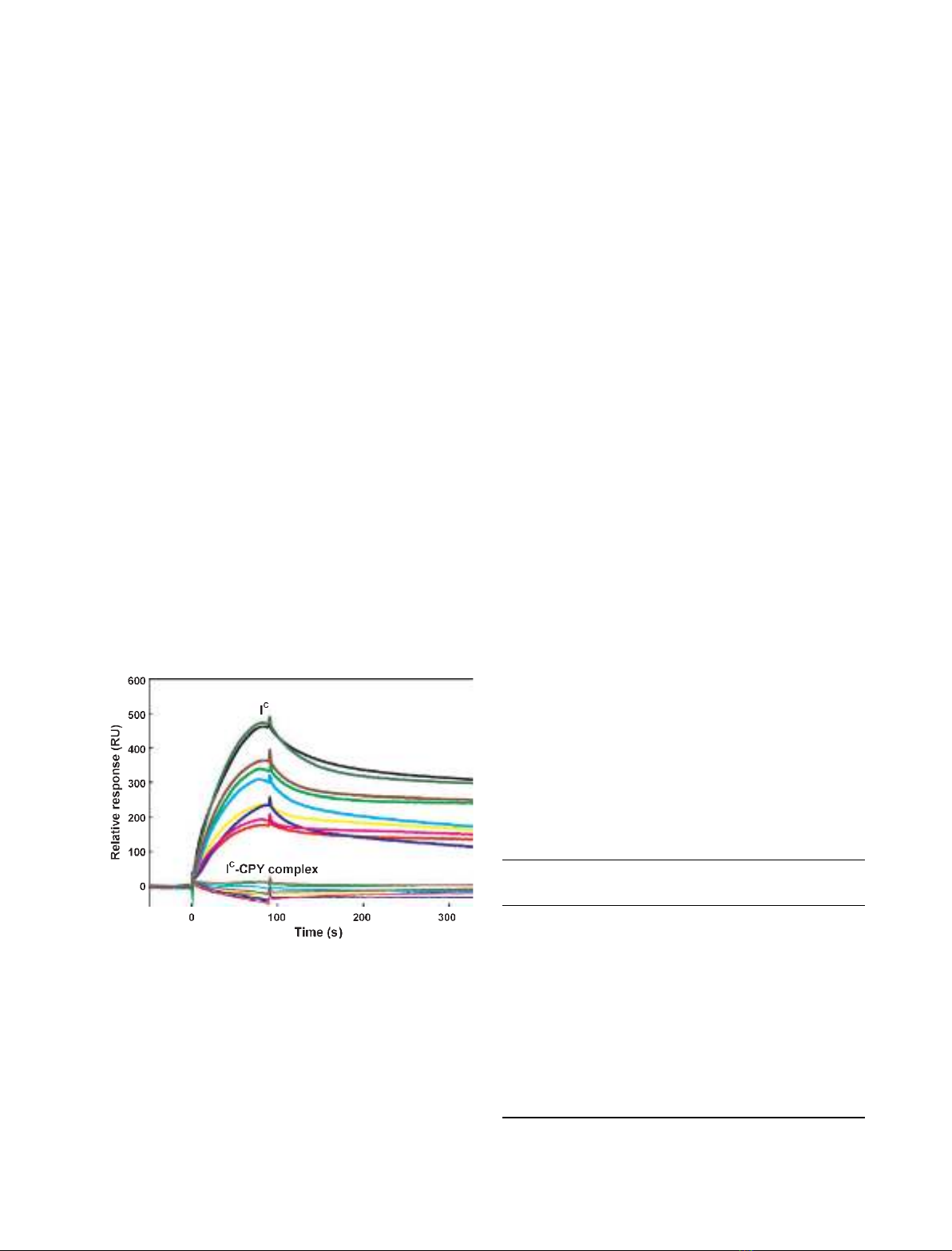
To further quantitatively evaluate the affinity and spe-
cificity of I
C
for phospholipid membranes, we next per-
formed SPR measurements, using this inhibitor as an
analyte and a number of the PC-based liposomes as a
ligand immobilized on the sensor surface of the L1 chip
[33]. Representative sensorgrams for the binding of I
C
to
the phospholipid liposomes showed that the inhibitor
has an affinity not only for PS ⁄PC and PtdIns ⁄PC,
which had been determined by the liposome-binding
assay, but also for other anionic phospholipid
liposomes, including phosphatidylglycerol (PG) ⁄PC,
phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PtdIns(3)P]⁄PC, phos-
phatidylinositol 4-phosphate [PtdIns(4)P]⁄PC, phos-
phatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate [PtdIns(3,4)P
2
]⁄PC,
phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(3,5)P
2
]⁄PC,
phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P
2
]⁄
PC, and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate
[PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
]⁄PC (Fig. 2). In contrast to the findings
with these liposomes, no binding was detected of I
C
to
the zwitterionic phospholipid liposomes PE ⁄PC and PC,
or to one of the anionic phospholipid liposomes, phos-
phatidylinositol 5-phosphate [PtdIns(5)P]⁄PC (data not
shown). In accordance with the liposome-binding assay
with I
C
–CPY (Fig. 1B,C), SPR responses of the complex
could not be detected toward all the phospholipid lipo-
somes (Fig. 2). These SPR analyses, as well as the lipo-
some-binding assay, demonstrated that I
C
, when
complexed with CPY, loses its intrinsic affinity for ani-
onic phospholipid membranes, and that the CPY-bind-
ing sites of I
C
[8] may be responsible for its phospholipid
recognition.
Using SPR sensorgrams for various concentrations
(0.1–10 lm)ofI
C
, the membrane association rate con-
stants (k
a
), dissociation rate constants (k
d
), and equi-
librium dissociation constants (K
D
) for the interaction
between the protein and PC-based liposomes, except
for PE, PC, and PtdIns(5)P(Table 1), were deter-
mined. A comparison of the membrane-binding
parameters indicates that I
C
exhibits a broad specificity
for a wide variety of anionic phospholipid membranes
with K
D
values below 600 nm, but has a slightly higher
affinity for PS, PtdIns(3)P, PtdIns(3,4)P
2
, and
PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
(K
D
values of 75–97 nm) than for
PtdIns, PG, and the other phosphoinositides (K
D
val-
ues of 200–550 nm) (Table 1). The lower affinity of I
C
for PtdIns and PG results mainly from the smaller
k
a
values, whereas the lower affinity for phosphoino-
sitides other than PtdIns(3)P, PtdIns(3,4)P
2
and
PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
results from the higher k
d
values.
Recent SPR studies of membrane–protein interactions
have shown that k
a
and k
d
are influenced by nonspe-
cific electrostatic interactions and proximal specific
interactions, respectively [34,35]. Those findings there-
fore suggest that nonspecific electrostatic interactions
between the negatively charged head groups of the
phospholipids, which include the carboxyl group of PS
and the phosphoryl groups of phosphoinositides, and
Fig. 2. SPR sensorgrams for membrane binding of I
C
and I
C
–CPY.
I
C
(bold solid lines) or I
C
–CPY (solid lines), the concentration of
which was 4 lM, was injected for 90 s over the surface of the L1
sensor chip coated with the phospholipid liposomes of PS ⁄PC
(black), PtdIns(4,5)P
2
⁄PC (green), PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
⁄PC (brown),
PG ⁄PC (lime), PtdIns(3,5)P
2
⁄PC (cyan), PtdIns(3)P⁄PC (yellow),
PtdIns(4)P⁄PC (blue), PtdIns(3,4)P
2
⁄PC (pink), or PtdIns ⁄PC (red).
All sensorgrams were obtained by SPR measurements in 20 mM
Hepes (pH 7.2) containing 0.15 MNaCl at 30 C, with a flow rate of
60 lLÆmin
)1
.
Table 1. Membrane-binding parameters for I
C
determined by SPR
analysis. Parameters represent mean ± SD from three or more
determinations. All SPR measurements were performed in 20 mM
Hepes (pH 7.2) containing 0.15 MNaCl at 30 C, with a flow rate of
60 llÆmin
)1
. PC-based liposomes (0.5 mgÆmL
)1
) were immobilized
on the L1 sensor chip. ND, not detectable.
Liposomes
k
a
(10
2
M
)1
Æs
)1
)
k
d
(10
)5
s
)1
)
K
D
(10
)9
M)
PE ⁄PC ND ND ND
PC ND ND ND
PS ⁄PC 80 ± 11 59 ± 3.9 75 ± 13
PtdIns ⁄PC 34 ± 9.8 70 ± 18 230 ± 94
PG ⁄PC 43 ± 2.4 85 ± 14 200 ± 24
PtdIns(3)P⁄PC 64 ± 23 60 ± 19 97 ± 26
PtdIns(4)P⁄PC 35 ± 12 180 ± 13 550 ± 190
PtdIns(5)P⁄PC ND ND ND
PtdIns(3,4)P
2
⁄PC 68 ± 13 60 ± 14 88 ± 7.6
PtdIns(3,5)P
2
⁄PC 68 ± 30 170 ± 42 280 ± 130
PtdIns(4,5)P
2
⁄PC 45 ± 8.4 89 ± 8.4 210 ± 57
PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
⁄PC 67 ± 3.9 50 ± 3.8 75 ± 5.3
Membrane binding of I
C
J. Mima et al.
5376 FEBS Journal 273 (2006) 5374–5383 ª2006 The Authors Journal compilation ª2006 FEBS

the positively charged residues of I
C
initially attract
the inhibitor to the membrane surface, and that the
membrane–protein interactions are then further stabil-
ized by short-range specific interactions, resulting in
the higher affinity for PS, PtdIns(3)P, PtdIns(3,4)P
2
,
and PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
.
Involvement of the CPY-binding sites of I
C
in its
membrane binding
As I
C
–CPY has no affinity for phospholipid membranes,
to obtain additional information on the involvement of
the CPY-binding sites of I
C
in its phospholipid recogni-
tion, we determined the membrane-binding parameters
for the mutant forms of I
C
, d1–7I
C
and d1–18I
C
, with
the N-terminal seven (Ac-MNQAIDF) and 18 (Ac-MN
QAIDFAQASIDSYKKH) residues, respectively, dele-
ted (Table 2). d1–7I
C
and d1–18I
C
lack the N-terminal
inhibitory reactive site (Ac-Met1–Phe7) [8] alone, and
both the N-terminal site and, in part, the secondary
CPY-binding site (Ala10–Gln70 and Phe133–Glu137)
[8], respectively. Prior to the SPR analyses, amino acid
sequencing, MS and CD spectroscopic analyses con-
firmed that the N-terminal residues were deleted in the
purified mutants of I
C
and that the mutant proteins were
correctly folded, forming the b-type gross structures
similar to the native protein (data not shown). SPR ana-
lyses of d1–7I
C
and d1–18I
C
showed that these mutants
of I
C
, as well as the native protein, were associated
with the anionic phospholipid liposomes of PS ⁄PC,
PtdIns ⁄PC and PG ⁄PC, and also the liposomes contain-
ing phosphoinositides rather than zwitterionic liposomes
of PE ⁄PC and PC (Table 2). However, the elimination
of the N-terminal residues significantly affects the bind-
ing parameters of I
C
with respect to these anionic
phospholipid liposomes. No binding of d1–7I
C
to
PtdIns(3)P⁄PC was detected, and the K
D
value of
d1–7I
C
binding to PtdIns(3,4)P
2
⁄PC was increased
13-fold. For the other liposomes, the K
D
values of the
mutant were also increased more than four-fold over
those of the native protein (Table 2). In contrast to
those of d1–7I
C
, the K
D
value of d1–18I
C
for
PtdIns(3,4)P
2
⁄PC was increased 2.4-fold, whereas the
K
D
values for PS ⁄PC, PtdIns ⁄PC, PG ⁄PC and
PtdIns(3)P⁄PC were increased 4.0–4.7-fold, and that for
PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
⁄PC was increased 8.1-fold (Table 2).
These results demonstrate that the N-terminal segment
of I
C
(Ac-Met1–His18) is essential for its binding effi-
ciency and specificity for phospholipid membranes and
suggest that the phospholipid recognition site of I
C
is
composed of residues in and adjacent to this N-terminal
segment.
Association of I
C
with cellular membranes
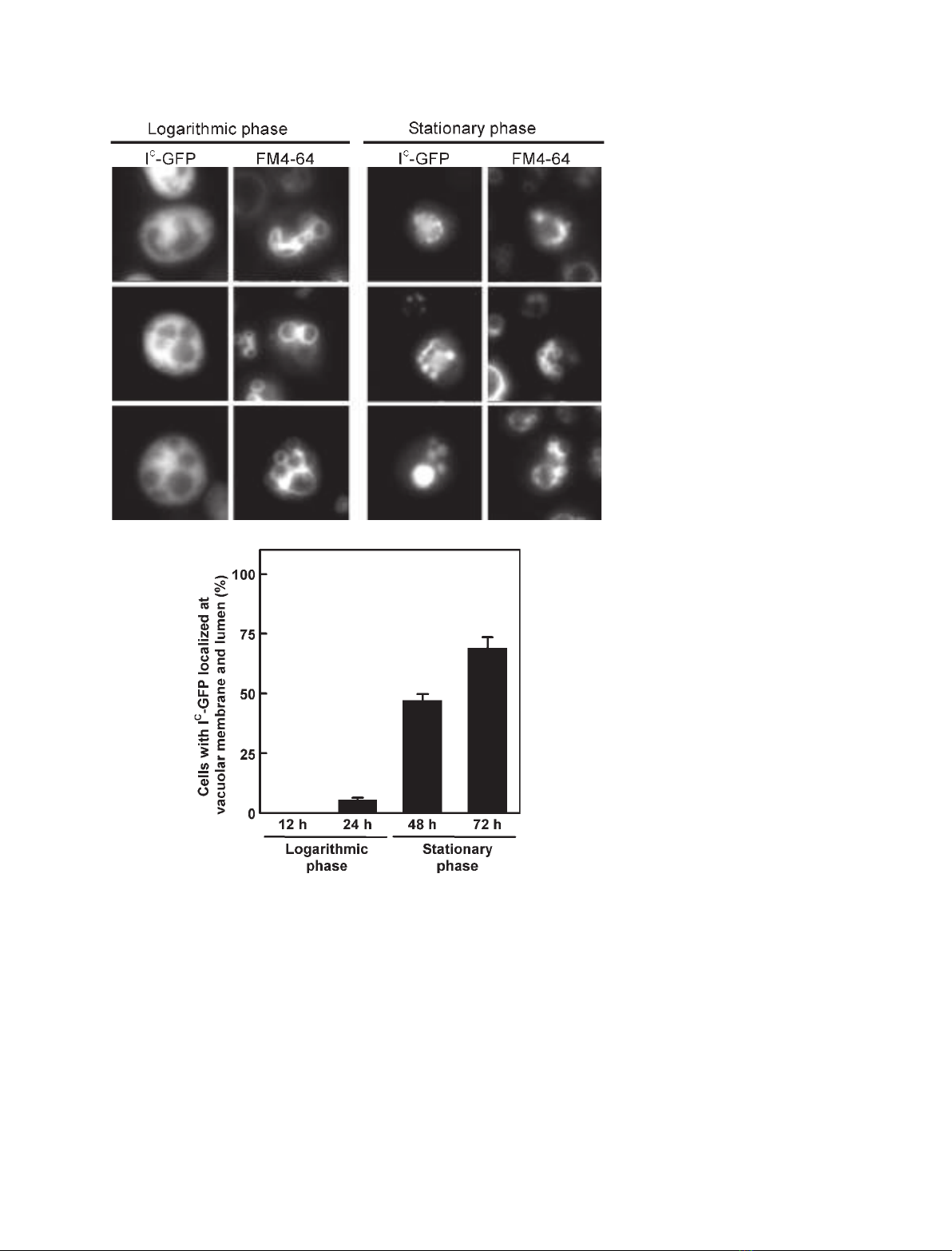
To gain insights into the association of I
C
with cellular
membranes, we subsequently examined the intracellular
localization of the inhibitor by fluorescence microscopy
of living yeast cells producing I
C
–GFP (Fig. 3). The
yeast cells were also labeled with N-(3-triethylammoni-
umpropyl)-4-(p-diethylaminophenylhexatrienyl) pyridi-
nium dibromide (FM4-64), a fluorescent dye used for
Table 2. Membrane-binding parameters for the mutant forms of I
C
with the N-terminal residues deleted, determined by SPR analysis.
Parameters represent mean ± SD from three or more determinations. All SPR measurements were performed in 20 mMHepes (pH 7.2)
containing 0.15 MNaCl at 30 C, with a flow rate of 60 llÆmin
)1
. PC-based liposomes (0.5 mgÆmL
)1
) were immobilized on the L1 sensor
chip. Increase in K
D
,K
D
for d1–7I
C
or d1–18I
C
⁄K
D
for I
C
. ND, not detectable.
Proteins Liposomes
k
a
(10
2
M
)1
Æs
)1
)
k
d
(10
)5
Æs
)1
)
K
D
(10
)9
M)
Increase in K
D
(fold)
d1–7I
C
PE ⁄PC ND ND ND –
PC ND ND ND –
PS ⁄PC 16 ± 3.7 56 ± 2.5 350 ± 93 4.7
PtdIns ⁄PC 10 ± 1.6 220 ± 36 2200 ± 630 9.6
PG ⁄PC 5.9 ± 0.44 91 ± 3.0 1600 ± 170 8.0
PtdIns(3)P⁄PC ND ND ND –
PtdIns(3,4)P
2
⁄PC 15 ± 9.1 150 ± 66 1100 ± 230 13
PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
⁄PC 16 ± 0.71 65 ± 7.6 400 ± 30 5.3
d1–18I
C
PE ⁄PC ND ND ND –
PC ND ND ND –
PS ⁄PC 24 ± 1.1 82 ± 23 350 ± 110 4.7
PtdIns ⁄PC 17 ± 5.3 150 ± 48 910 ± 290 4.0
PG ⁄PC 18 ± 3.3 160 ± 4.0 890 ± 160 4.5
PtdIns(3)P⁄PC 46 ± 4.4 200 ± 14 430 ± 68 4.4
PtdIns(3,4)P
2
⁄PC 49 ± 24 80 ± 10 200 ± 110 2.4
PtdIns(3,4,5)P
3
⁄PC 25 ± 1.7 150 ± 20 610 ± 110 8.1
J. Mima et al.Membrane binding of I
C
FEBS Journal 273 (2006) 5374–5383 ª2006 The Authors Journal compilation ª2006 FEBS 5377
staining vacuolar membranes that was taken up by
endocytosis. A western blotting analysis using an anti-
body to GFP showed that the full-length protein of I
C
–
GFP was correctly produced in the yeast cells at com-
parable levels during both the logarithmic (12 h and
24 h) and stationary (48 h and 72 h) growth phases
(data not shown). The observed fluorescence of I
C
–
GFP was in the extravacuolar cytoplasmic fraction in
the logarithmic growth phase (the left panels of
Fig. 3A). However, in the stationary growth phase, the
fluorescence of I
C
–GFP was observed at the FM4-64-
stained vacuolar membranes and also the vacuolar
lumens in the majority of yeast cells (70% of the cells
grown at 72 h; right panels of Fig. 3A,B). Therefore,
the fluorescence microscopic analyses clearly demon-
strate that I
C
–GFP present in the cytoplasm during the
logarithmic growth phase was selectively relocalized at
the vacuolar membranes and lumens during the station-
ary phase.
Discussion
PEBP from bovine brain, a mammalian homolog of I
C
,
was originally isolated as a 23 kDa cytoplasmic protein
A
B
Fig. 3. Fluorescence microscopic analyses
of yeast cells producing I
C
–GFP. (A) Repre-
sentative fluorescence images. S. cerevisiae
BY4741icDcells producing I
C
–GFP were
labeled with the vacuolar membrane fluores-
cent dye FM4-64, and harvested at the log-
arithmic (12–24 h) and stationary (48–72 h)
growth phases. The localization of I
C
–GFP
and FM4-64 was visualized and compared
by fluorescence microscopy. (B) Quantitation
of intracellular localization of I
C
–GFP. Cells
(n> 100 ⁄group) at the logarithmic and sta-
tionary phases were scored for the localiza-
tion of I
C
–GFP at the vacuolar membrane
and lumen or in the cytoplasm. Error bars
indicate SE.
Membrane binding of I
C
J. Mima et al.
5378 FEBS Journal 273 (2006) 5374–5383 ª2006 The Authors Journal compilation ª2006 FEBS


























