
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited
Describing Consumer
Describing Consumer
Preferences Using
Preferences Using
Indifference Curves
Indifference Curves
Chapter 8 Appendix
Chapter 8 Appendix

© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
8A - 2
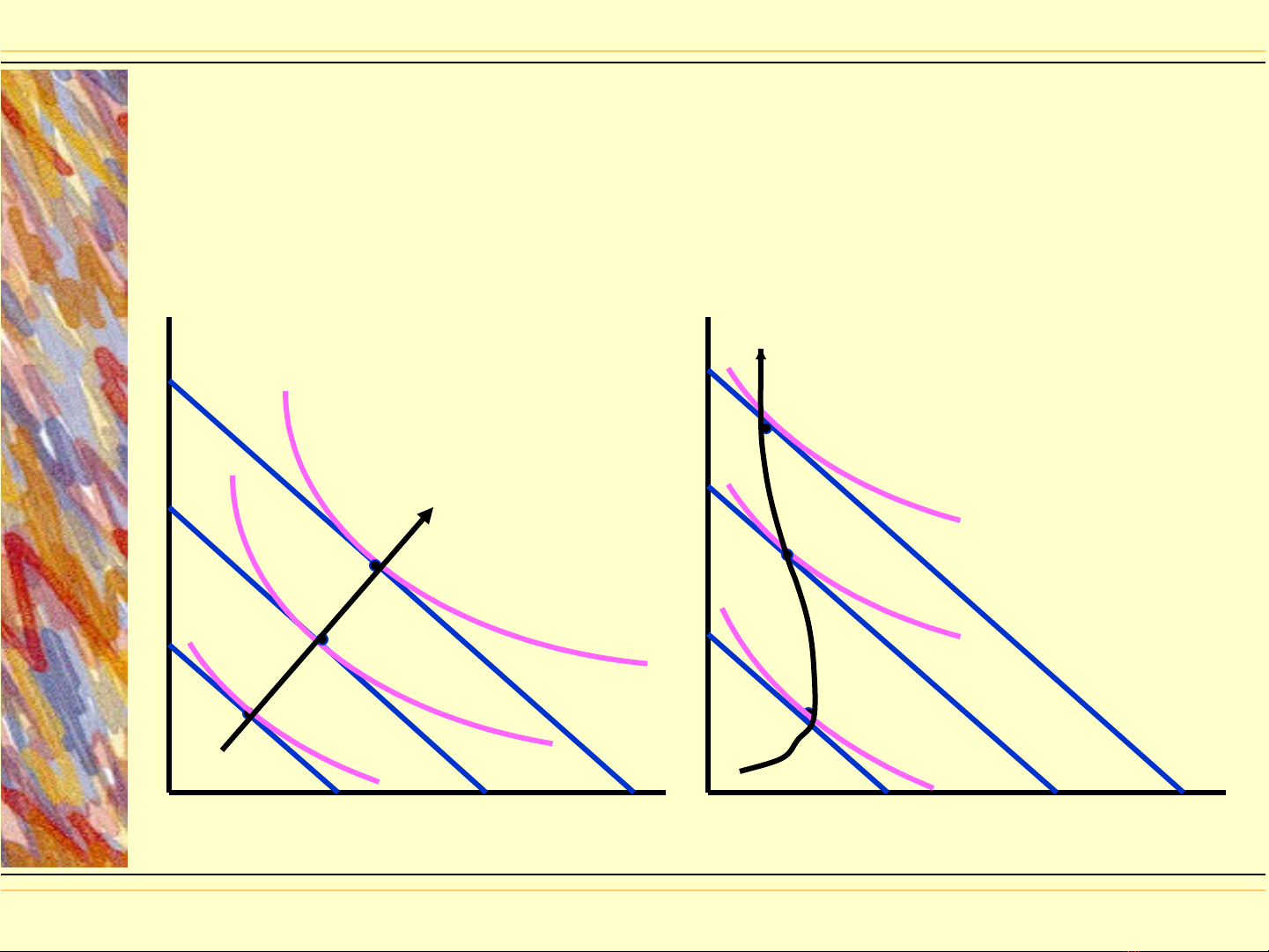
Income expansion path
Income expansion path
◆Income expansion path -IEP- traces all
the best (utility-maximizing) choices a
consumer makes as income changes.
●The IEP slopes up if a good is a normal good
●The IEP is downward sloping if a good is
inferior
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
8A - 3
Income expansion path,
Income expansion path, Fig. A8-1 a and
Fig. A8-1 a and
b, p 195
b, p 195
U1
U2
U3
U3
U2
U1
IEP
IEP
Good Y Good Y
Good X Good X
a) Normal good a) Inferior good

© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
8A - 4
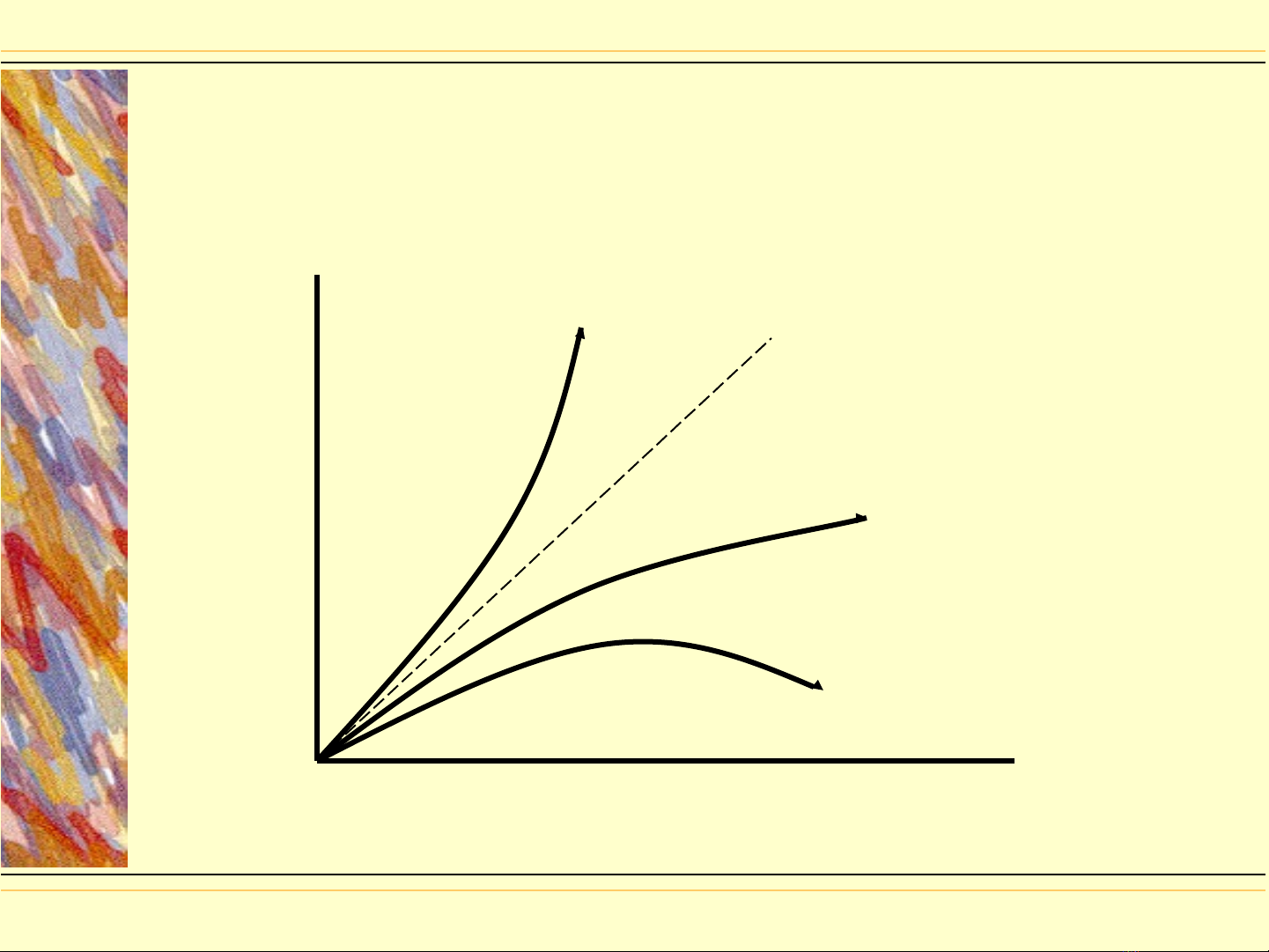
Engel Curves
Engel Curves
◆An Engel curve plots all the best
choices a consumer makes against
INCOME.
●It is an income-quantity relationship
◆If an Engel curve is upward sloping, a
good is normal; downward sloping
indicates an inferior good.
© 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.
8A - 5
Engel Curves,
Engel Curves, Fig. A8-2, p 195
Fig. A8-2, p 195
Quantity
demanded
Income
X1
X2
X3
Income elastic normal good
(luxury)
Income inelastic
normal good
(necessity)
Inferior good






![Chính Sách Hỗ Trợ Vốn Cho Sinh Viên Việt Nam Hiện Nay: [Mô tả/Định tính Thêm để Tăng CTR]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2013/20131116/nobita_12/135x160/5551384572371.jpg)



![Bài giảng Kế toán tài chính 2: Chương 1 - Trường ĐH Ngân hàng [Mới Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260121/hoatrami2026/135x160/62991769067201.jpg)


![Giáo trình Kế toán thương mại dịch vụ: Phần 1 - TS. Hoàng Thị Hồng Lê [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260121/hoatrami2026/135x160/23861769066575.jpg)











