
Secretion of a peripheral membrane protein, MFG-E8,
as a complex with membrane vesicles
A possible role in membrane secretion
Kenji Oshima
1
, Naohito Aoki
1
, Takeo Kato
2
, Ken Kitajima
1
and Tsukasa Matsuda
1
1
Graduate School of Bioagricultural Sciences, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan;
2
Food Research Institute, Aichi Prefectural
Government, Nagoya, Japan
MFG-E8 (milk fat globule-EGF factor 8) is a peripheral
membrane glycoprotein, which is expressed abundantly in
lactating mammary glands and is secreted in association with
fat globules. This protein consists of two-repeated EGF-like
domains, a mucin-like domain and two-repeated discoidin-
like domains (C-domains), and contains an integrin-binding
motif (RGD sequence) in the EGF-like domain. To clarify
the role of each domain on the peripheral association with
the cell membrane, several domain-deletion mutants of
MFG-E8 were expressed in COS-7 cells. The immunofluo-
rescent staining of intracellular and cell-surface proteins and
biochemical analyses of cell-surface-biotinylated and secre-
ted proteins demonstrated that both of the two C-domains
were required for the membrane association. During the
course of these studies for domain functions, MFG-E8, but
not C-domain deletion mutants, was shown to be secreted as
membrane vesicle complexes. By size-exclusion chromato-
graphy and ultracentrifugation analyses, the complexes were
characterized to have a high-molecular mass, low density
and higher sedimentation velocity and to be detergent-
sensitive. Not only such a exogenously expressed MFG-E8
but also that endogenously expressed in a mammary epi-
thelial cell line, COMMA-1D, was secreted as the membrane
vesicle-like complex. Scanning electron microscopic analyses
revealed that MFG-E8 was secreted into the culture medium
in association with small membrane vesicles with a size from
100 to 200 nm in diameter. Furthermore, the expression of
MFG-E8 increased the number of these membrane vesicle
secreted into the culture medium. These results suggest a
possible role of MFG-E8 in the membrane vesicle secretion,
such as budding or shedding of plasma membrane (micro-
vesicles) and exocytosis of endocytic multivesicular bodies
(exosomes).
Keywords: MFG-E8; membrane secretion; exosome; per-
ipheral membrane protein; milk fat globule membrane.
MFG-E8 (milk fat globule-EGF factor 8) was cloned and
characterized as mouse milk 53- and 66-kDa glycoproteins
peripherally associated with the membrane surrounding the
lipid droplets and being referred to as milk fat globule
membrane (MFGM) [1]. MFG-E8 consists of two repeated
EGF-like domains on the N-terminal side and of two
repeated C (discoidin-like) domains homologous to the C1
and C2 domains of blood coagulation factors V and VIII.
Orthologous proteins have been isolated in bovine
(MGP57/53 or PAS-6/7) [2,3], human (BA46 or lacta-
dherin) [4,5] and rat (rAGS) [6].
Though the expression of MFG-E8 is upregulated in
lactating mammary gland, MFG-E8 has also been detected
in various other tissues, including brain, lung, heart, kidney
and spleen in some mammals such as mouse, human and
bovine [7–9]. The mouse and bovine MFG-E8 proteins
expressed in mammary gland were shown to be composed
of two isoforms [3,9]. In mouse, a Pro/Thr-rich domain is
inserted possibly by a mammary gland-specific alternative
splicing between EGF-like and C-domains, resulting in the
production of a long form of MFG-E8 (MFG-E8-L) in the
lactating mammary gland. In contrast, a short form (MFG-
E8-S) lacking the Pro/Thr-rich domain is ubiquitously
expressed in various tissues [9].
The second EGF-like domain of MFG-E8 contains an
integrin-binding Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) sequence motif [10],
which is conserved in all known MFG-E8 sequences of
several species and binds to some integrins. The avb5
integrin was affinity-purified from lactating bovine udder
extracts by using its specific binding to bovine milk
MFG-E8 [7], and human and bovine MFG-E8 proteins
promoted cell adhesion through avb3andavb5 integrins
[11, 12]. Although MFG-E8 contains no apparent hydro-
phobic transmembrane regions, MFG-E8 has been shown
to be a peripheral membrane protein and bind directly to
the MFGM and cell membrane [7,13–15]. Both the native
and recombinant MFG-E8 proteins bind in vitro to anionic
phospholipids, especially phosphatidylserine (PtdSer)
[7,12,16]. This PtdSer-binding of MFG-E8 has been
reported to depend only on the second C-domain
(C2-domain), but not the first C-domain (C1-domain),
in the same manner as that of blood coagulation factors
V and VIII [17–19].
Correspondence to T. Matsuda, Department of Applied Molecular
Biosciences, Graduate School of Bioagricultural Sciences, Nagoya
University, Furo-cho, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya 464-8601, Japan.
Fax: + 81 52 789 4128, Tel.: + 81 52 789 4129,
E-mail: tmatsuda@agr.nagoya-u.ac.jp
Abbreviations: MFGM, milk fat globule membrane; DMEM,
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s serum; DAPI, 4¢,6-diamidine-2-phenyl-
indole-dihydrochloride; ECL, enhanced chemiluminescence; MVBs,
endocytic multivesicular bodies; GST, glutathione S-transferase.
(Received 19 September 2001, revised 17 December 2001, accepted 2
January 2002)
Eur. J. Biochem. 269, 1209–1218 (2002) ÓFEBS 2002

Recently, MFG-E8 was detected as the major component
of the secretory membrane vesicle (exosome) secreted by a
murine dendritic cell line (D1) [20]. Furthermore, a glioma
cell line (C6) has also been shown to secrete MFG-E8 into
the culture media [21]. MFG-E8 is also detected extracell-
ularly in embryonic gonad [22] and in sera of patients with
breast tumor metastasis [23]. Thus, the results reported so
far suggest that MFG-E8 secreted extracellularly, at least in
some occasions, despite the membrane associated nature of
MFG-E8. Aims of the present study are to elucidate cellular
and extracellular distribution of MFG-E8 expressed in
cultured mammalian cells and to identify domain(s)
responsible for the membrane association and/or secretion.
By using transformed COS-7 cells as well as a mammary
epithelial cell line, COMMA-1D expressing MFG-E8, we
have found that MFG-E8 exists not only on the cell surface
but also in association with uncharacterized membrane
vesicles secreted into culture medium. The expression of
several domain-deletion mutants of MFG-E8 suggests
contribution of the C2 domain to the association with
PtdSer and plasma membrane and subcontribution of the
C1 domain to the association with plasma membrane.
A possible role of MFG-E8 in the vesicular secretion is also
discussed.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Cell culture
A mouse mammary epithelial cell line, COMMA-1D, and a
monkey kidney cell line, COS-7 were cultured in Dulbecco’s
modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM, Sigma) containing
10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, penicillin at
100 UÆmL
)1
, streptomycin at 100 lgÆmL
)1
at 37 °C under
humidified 5% CO
2
and 95% air.
Construction of expression plasmids
and gene transfection
MFG-E8-L and -S expression plasmids were generated as
described previously [9]. A truncated MFG-E8-L cDNA
that lacks a region encoding the C1 domain (amino acids
147–306) was constructed as follows. The cDNA fragments
upstream and downstream of the C1 domain were amplified
by PCR using the MFG-E8-L expression plasmid as a
template with primer sets containing an XbaI site as follows:
5¢-ATGCAGGTCTCCCGTGTGC-3¢,5¢-ATTCTAGAG
GCTAGGTTGTTGGAAAG-3¢,5¢-ATTCTAGAGGAT
GTCTTGAGCCCCTG-3¢and 5¢-TTCTCGAGCAGGA
CTGAGCATTAACAG-3¢. The two DNA fragments were
ligated at the XbaI site and inserted into a cloning vector
pBluescript KS(+) (Stratagene). As a result of the ligation,
the domain to be deleted was replaced by two amino acids,
serine and arginine, which were translated from the XbaI-
site sequence TCTAGA. The cDNA lacking the C1 domain
was then amplified by PCR from the cloned plasmid
with primers containing an EcoRI site at the 5¢end
(5¢-TAGAATTCCACCATGCAGGTCTCCCGT-3¢)and
an EcoRV site at the 3¢end (5¢-CAGATATCTTAACAGC
CCAGCAGCTC-3¢). The cDNA lacking the C2 domain
(amino acids 307–463) was created by PCR directly from
the MFG-E8-L expression plasmid with primers containing
an EcoRI site at the 5¢end as same above and an EcoRV
site at the 3¢end (5¢-CAGATATCTTAGTGCAACTCAC
AGCC-3¢). The two PCR products were cloned into a
mammalian expression vector, pEF1/Myc-His C (Invitro-
gen), at EcoRI and EcoRV sites, respectively, and were
checked by sequencing for PCR errors.
COS-7 cells were seeded at a density of 2.5 ·10
5
cells per
60-mm dish, and grown overnight in DMEM containing
10% fetal bovine serum. The cells were transfected with the
plasmid DNA by the calcium phosphate-DNA precipita-
tion method [24]. After incubation under 3% CO
2
and 97%
air for 18 h, the transfected cells were washed with NaCl/P
i
and cultured under humidified 5% CO
2
and 95% air.
Immunofluorescence staining
COS-7 cells were cultured on cover glasses and transfected
with MFG-E8s expression plasmids as described above.
After being cultured in DMEM containing 10% fetal
bovine serum for 24 h, cells were washed three times with
NaCl/P
i
andfixedwith3%paraformaldehydeinNaCl/P
i
for 8 min for extracellular staining or with methanol chilled
at )20 °C for 5 min for intracellular staining. After blocking
with NaCl/P
i
containing 2% BSA (blocking solution) for
30 min, the specimens were incubated for 60 min with the
rabbit antiserum raised against the recombinant glutathione
S-transferase (GST)–MFG-E8 fusion protein [8] diluted
1 : 150 in blocking solution and then incubated for 30 min
with the secondary antibody, FITC-labeled goat anti-
(rabbit IgG) Ig (ICN/Cappel). Samples were then incubated
for 15 min with 4¢,6-diamidine-2-phenylindole-dihydrochlo-
ride (DAPI) (Roche Molecular Biochemicals) (1 lgÆmL
)1
NaCl/P
i
) and washed three times with NaCl/P
i
.Imageswere
acquired by using a fluorescence microscope (Olympus).
SDS/PAGE and Western blotting
The transfected cells were cultured in serum-free DMEM
for 24 h and then lysed with Ôlysis bufferÕcontaining 50 m
M
Hepes (pH 7.5), 150 m
M
NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1% Triton
X-100, 5 m
M
EDTA, 1 m
M
phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride
and 10 lgÆmL
)1
leupeptin. The culture supernatant of the
transfected COS-7 cells was concentrated to one-sixtieth of
its original volume by centrifugal filtration through the M
r
10 000 cut-off membrane (Amicon). Proteins in the cell
lysate and the culture medium were separated by SDS/
PAGE (10% acrylamide gel) and electrophoretically trans-
ferred to the membrane Immobilon-P (Millipore). The
membrane was blocked and then sequentially incubated
with the rabbit anti-(GST–MFG-E8) serum and peroxi-
dase-conjugated goat anti-(rabbit IgG) Ig. The protein
bands probed with the peroxidase-labeled antibody were
visualized with an enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL)
detection kit (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech).
Cell surface biotinylation
COS-7 cells were plated onto six-well polystyrene plates at a
density of 1 ·10
5
cells per well and transfected with the
MFG-E8 expression plasmids as described above. After
incubation in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine
serum for 48 h, the cells were washed three times with
cold NaCl/P
i
and incubated at 4 °C for 30 min in the
presence of 0.5 mgÆmL
)1
Sulfo-N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide-
1210 K. Oshima et al. (Eur. J. Biochem. 269)ÓFEBS 2002

Biotin (Pierce). After nonreacted biotin was quenched with
serum-free DMEM at 4 °C for 5 min, cells were washed
three times with NaCl/P
i
and then lysed with the lysis buffer.
Streptavidin–Sepharose (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech)
was added to the cell lysate and incubated overnight at
4°C. Proteins bound to the Sepharose were precipitated
by centrifugation and washed extensively with a buffer
containing 50 m
M
Hepes (pH 7.5), 150 m
M
NaCl,
10% glycerol, 0.1% Triton X100 and then subjected to
SDS/PAGE followed by Western blotting.
Size-exclusion chromatography of the secreted MFG-E8
Culture supernatants from the transfected COS-7 cells
(8 ·10
6
cells) grown in serum-free DMEM for 24 h were
concentrated as described above. The concentrated super-
natants (500 lL) were subjected to the size-exclusion
chromatography using a Sephacryl S-300 column
(0.9 ·60 cm), equilibrated with NaCl/P
i
. The elution
profiles of MFG-E8 and its mutants were monitored by
ELISA. ELISA plate was coated directly with each fraction,
and the antigens were detected by using the rabbit anti-
(GST–MFG-E8) serum and peroxidase-conjugated goat
anti-(rabbit IgG) Ig as described previously [25].
Ultracentrifugation
Culture supernatants from COMMA-1D cells (8 ·10
6
cells) and the transfected COS-7 cells (4 ·10
6
cells) were
prepared and concentrated as described above. Aliquots
(500 lL) of the concentrated samples were clarified by
sequential centrifugation at 1200 g(10 min) and 10 000 g
(30 min) to eliminate cells and debris. In the experiment to
examine the effect of detergent, 50 lL of 10% Triton X-100
was then added to the supernatants of the centrifugation,
followed by the incubation on ice for 10 min. These samples
with or without Triton X-100 were ultracentrifuged at
100 000 gfor 1 h at 4 °C. The resulting supernatants were
recovered, while the pellets were resuspended in 100 lLof
NaCl/P
i
containing 0.01% sodium azide and 10 lgÆmL
)1
leupeptin. The presence of MFG-E8 was determined by
Western blotting for both of the supernatants and pellets.
Sucrose density-gradient ultracentrifugation
Culture supernatants from the transfected COS-7 cells
(8 ·10
6
cells) were prepared and concentrated as described
above. Concentrated samples (500 lL) were mixed with
2.5 vol. of buffer A [85% (w/v) sucrose in 10 m
M
Tris/HCl
(pH 7.5) containing 150 m
M
NaCl and 5 m
M
EDTA], and
placed in centrifuge tubes. The mixtures were layered
successively with 4 mL of 60% (w/v), 3 mL of 30% (w/v)
and 1 mL of 5% (w/v) sucrose in buffer A, and centrifuged
at 200 000 gfor 18 h at 4 °C (Beckman L-70K centrifuge,
SW41 Ti rotor). The fractions with different densities were
collected with 1 mL portions from the top to the bottom of
the tube. Each fraction was directly subjected to SDS/
PAGE followed by Western blotting.
Phospholipid-binding assay by ELISA
The ELISA for MFG-E8 binding to solid-phase phospho-
lipid was performed as described previously [7].
L
-a-phosphatidyl-
L
-serine (Sigma) in methanol
(10 lgÆmL
)1
) was added to a micro well plate (Nunc)
(30 lLÆwell
)1
) followed by drying at 37 °C. The plate was
washed three times between all subsequent steps with NaCl/
Tris containing 0.05% Tween-20. The plate was blocked
with 200 lL of NaCl/Tris containing 0.05% (w/v) gelatine
(blocking buffer). Culture supernatants of the transfected
COS-7 cells were concentrated to one-fourth of its original
volume. Appropriate amounts of total proteins in the
supernatants were then diluted in 50 lL of blocking buffer,
and were added per well, followed by incubation at 4 °C
overnight. The plate was then incubated with anti-(GST–
MFG-E8) serum and peroxidase-labeled goat anti-(rabbit
IgG) Ig as the secondary antibody, and peroxidase activity
was measured.
Scanning electron microscopy
Samples for scanning electron microscopy analysis were
prepared essentially as previously described for microvesi-
cles [26]. Culture supernatants of the transfected COS-7 cells
(2 ·10
6
cells) cultured in serum-free DMEM for 48 h were
centrifuged at 10 000 gfor 30 min to eliminate cells and
debris. The supernatants were then centrifuged at 200 000 g
for 1.5 h at 4 °C. The pellets were resuspended in 100 lLof
NaCl/Tris with 0.01% sodium azide and 10 lgÆmL
)1
leupeptin. The suspended samples were placed onto micro-
scope glass slides, previously treated with poly
L
-lysine
(Sigma) for 30 min, and then fixed with 1% OsO
4
for
2 h. The samples were dehydrated in a series of ethanol
(50–100%), critical-point dried in a CO
2
system. After being
platinum/palladium-coated in a spattering devise, the speci-
mens were observed with a scanning electron microscope
(JSM-820, Japan Electron Optics Laboratory).
RESULTS
Cellular and extracellular distribution of MFG-E8
and its domain deletion mutants expressed in COS-7 cells
To investigate cell surface distribution of MFG-E8 and
contribution of each domain to the cellular localization,
several domain-deletion mutant genes for MFG-E8 was
constructed (Fig. 1) and transiently expressed in COS-7
cells. The transfected cells were fixed, and the cell surface
and intracellular MFG-E8 proteins were detected by
indirect immunofluorescence staining using the antibody
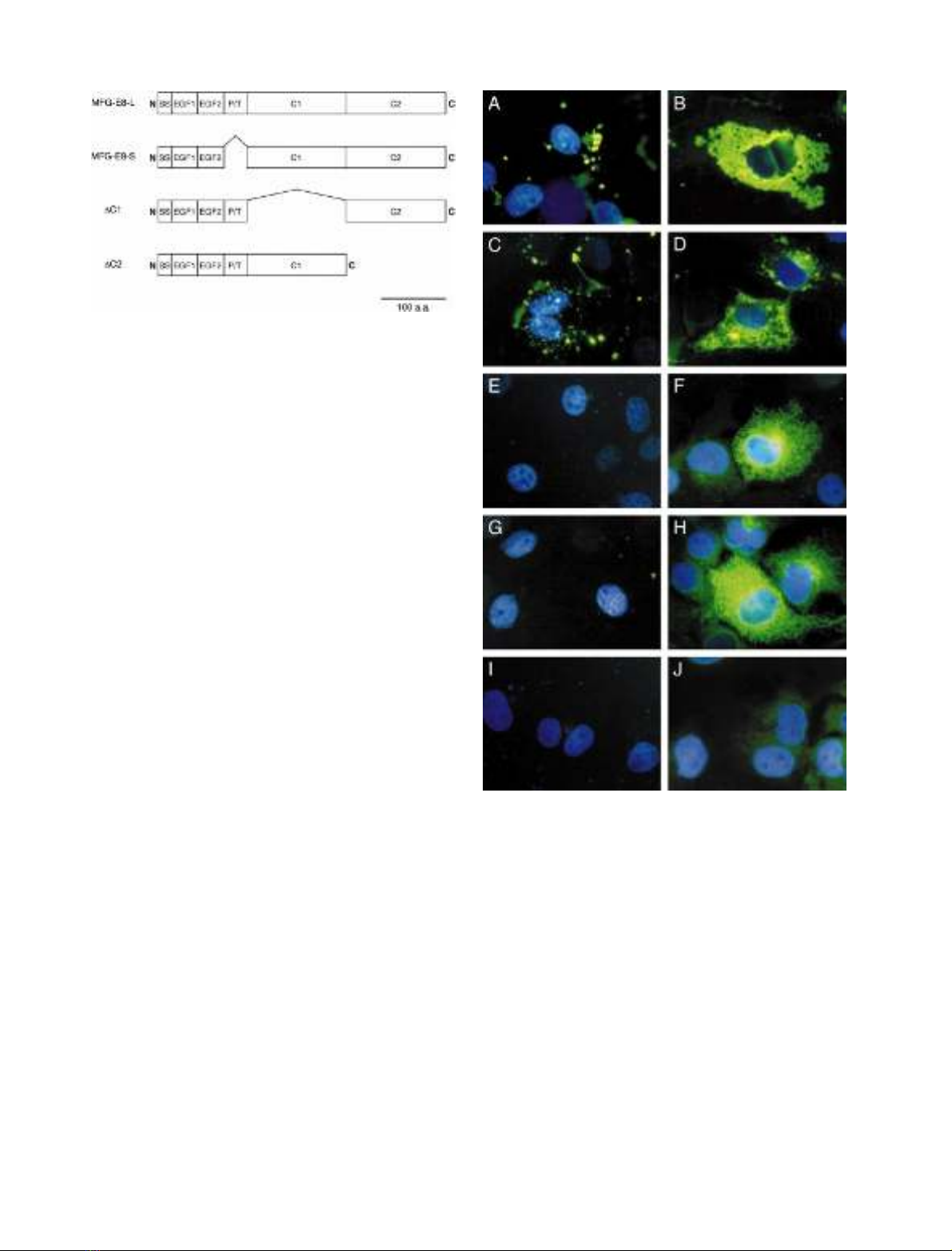
specific for MFG-E8. As shown in Fig. 2, under a
nonpermeable condition the two wild-type MFG-E8
proteins (MFG-E8-L and -S) were detected as many dots
on the surface of transfected cells, whereas no signal was
detected for the two C-domain deletion mutants (DC1 and
DC2). Under permeable conditions, however, all of MFG-
E8 and deletion mutants were clearly detected in cyto-
plasm. No signal was detected under permeable or
nonpermeable conditions for an empty-vector (mock)
transfectant. Thus, MFG-E8, expressed in COS-7 cells,
localized on the cell surface and both of the two
C-domains were indispensable for such a cell surface
localization of MFG-E8. A possibility that cytosolic
MFG-E8 was stained under the nonpermeable condition
could be excluded because DC1 and DC2 were not
detected under the same condition.
ÓFEBS 2002 MFG-E8: a component of secreted membrane vesicles (Eur. J. Biochem. 269) 1211
As the expression and localization of MFG-E8 and its
deletion mutants in COS-7 cells was revealed immunocyto-
chemically, biochemical analyses including cell surface
biotinylation were done subsequently for both of the
transfected cells and their culture supernatants. As shown
in Fig. 3, MFG-E8-L and -S were clearly labeled by the cell
surface biotinylation, confirming their existence on the cell
surface. In contrast, only weak or almost no bands were
detected for the C-domain deletion mutants, indicating that
they did not retain on the cell surface. When the culture
supernatants were analyzed, considerable amounts of the
C-domain deletion mutants were found to be secreted into
the culture medium. Furthermore, MFG-E8-L and -S were
detected in culture supernatant, indicating that they were
not only plasma-membrane-associated but also secreted.
While three size-variants (66, 56 and 51 kDa) for MFG-E8-L
were detected in the total cell lysate and cell-surface
biotinylated proteins, secreted MFG-E8-L was only a single
band of 66 kDa. On the other hand, the molecular mass of
MFG-E8-S was 51 kDa regardless its secretory or cellular
form. Both of DC1 (47 kDa) and DC2 (43 kDa) in the
culture media were markedly larger in size than those of
cellular forms in the cell lysate (38 and 34 kDa).
The MFG-E8, but not the C-domain deletion mutants,
is secreted as a constituent of high-molecular mass
complex and binds to phosphatidylserine
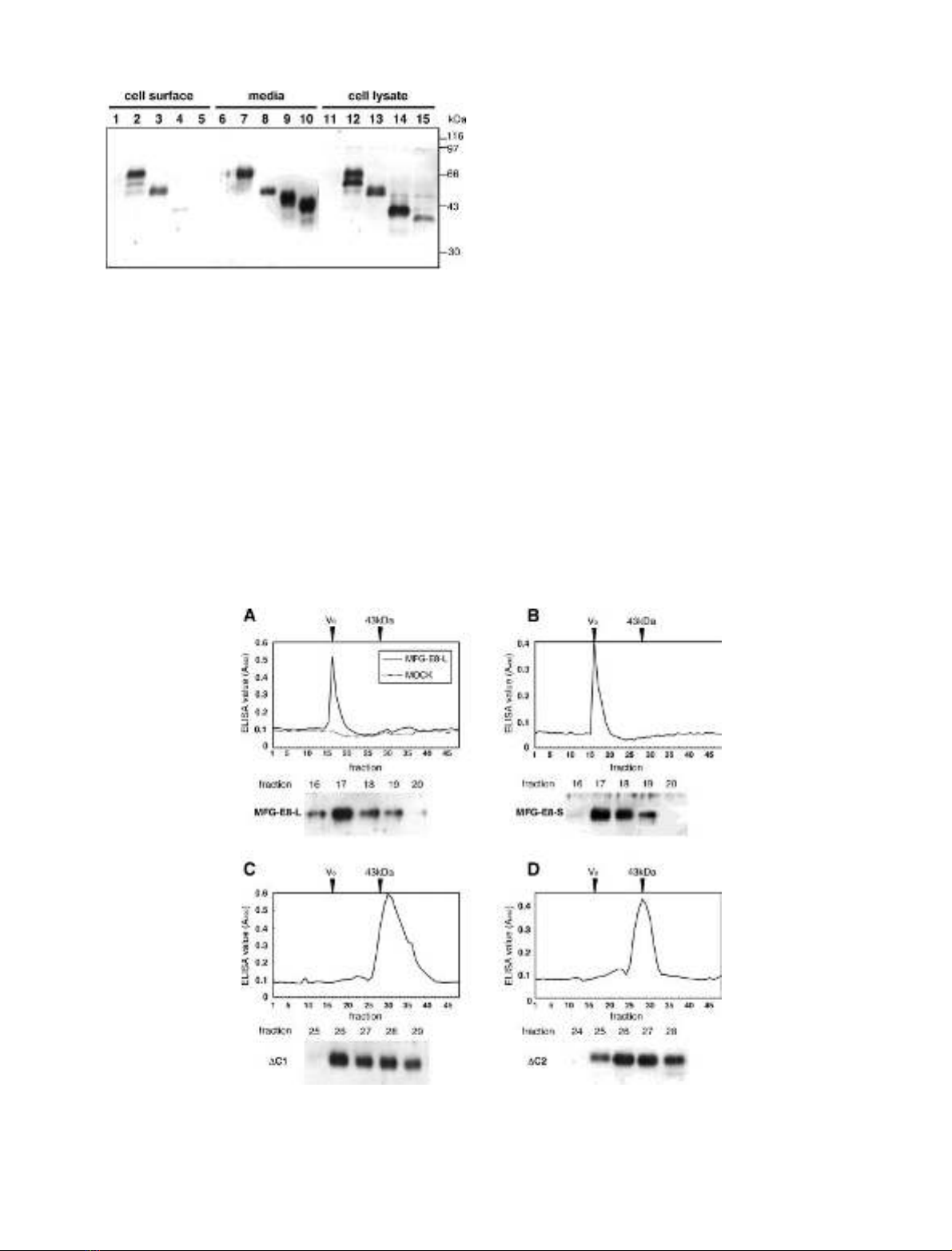
Molecular sizes of the MFG-E8-L, -S and its C-domain
deletion mutants secreted in the culture medium were
estimated by size exclusion chromatography using a
Sephacryl S-300 column (Fig. 4). Both of the ELISA and
immunoblot analysis revealed that the wild-type proteins,
MFG-E8-L and -S, were eluted in the void volume fractions
(fraction numbers 16–18) much earlier than expected.
Therefore, the secreted MFG-E8 was found to behave as
high molecular mass complex(es). On the other hand, the
C-domain deletion mutants were eluted in fractions 26–28,
which corresponded to the elution volume for a 43-kDa
protein (ovalbumin). The molecular masses estimated for
the C-domain deletion mutants by this size exclusion
chromatography agreed well with those by SDS/PAGE
(Fig. 3), indicating that the secreted DC1 and DC2 proteins
were monomeric. When the elution profiles of the two
C-domain deletion mutants were compared, the peak of
DC1 was obviously broader than that of DC2.
In some previous reports, the C2 domain of MFG-E8 as
well as that of blood clotting factors V and VIII has been
shown to be a binding-domain to PtdSer or PtdSer-rich
Fig. 2. Cell surface localization of MFG-E8 depending on the
C-domains. COS-7 cells were transfected with plasmids containing
MFG-E8-L (A and B), MFG-E8-S (C and D), DC1 (E and F) and DC2
(G and H) or empty plasmid (I and J). Transfectants were fixed and
stained with the antiserum specific for MFG-E8 followed by FITC-
labeled secondary antibodies. The immunostaining was done with
permeabilization (B, D, F, H and J) or without (A, C, E, G and I). The
cells were also stained with DAPI to visualize nuclei. Note that only
two wild-type MFG-E8s containing both of two C-domains (A and C)
were stained on cell surface, whereas intracellular MFG-E8 was
stained for all of the transfectants (B, D, F and H).
Fig. 1. A schematic representation of MFG-E8 and its mutant proteins.
MFG-E8-L, a long form (a lactation mammary grand specific form) of
MFG-E8; MFG-E8-S, a short form (an ubiquitous form) of MFG-E8;
DC1, MFG-E8-L lacking C1 domain; DC2, MFG-E8-L lacking C2
domain. Signal sequence (SS), tandem EGF-like repeat (EGF1,
EGF2) and Pro/Thr-rich domain followed by two C-domains (C1, C2)
are shown.
1212 K. Oshima et al. (Eur. J. Biochem. 269)ÓFEBS 2002
membrane [8,12,16]. Therefore, the PtdSer-binding ability
of the secreted MFG-E8 and its C-domain deletion mutants
was examined by ELISA using polystylene microtiter plate
coated with PtdSer. MFG-E8-L and -S as well as DC1
showed the PtdSer-binding in a concentration-dependent
manner (Fig. 5). The DC2 protein, however, did not bind to
the PtdSer-coated plates even at higher concentrations.
The high molecular mass complexes containing MFG-E8
are membrane-derived vesicles
The high molecular mass of secreted forms of MFG–E8
suggested certain interaction of an MFG-E8 molecule with
some other molecule(s) including MFG-E8 itself in a case of
homophilic association. To determine whether the secreted
MFG-E8 associates with proteins or other components
such as lipid, phospholipid and membrane vesicle, the
culture supernatant was ultracentrifuged at 100 000 gin the
presence or absence of a nonionic detergent, Triton X-100,
and then both of the precipitate and supernatant were
subjected to Western blotting analysis for MFG-E8. As
shown in Fig. 6, in the absence of the detergent, about a half
of the secreted MFG-E8 or more was precipitated under
this centrifugation condition, whereas DC2 was not. The
sizes of MFG-E8-L, -S and DC2 bands seen in the
precipitates or supernatants were consistent with those of
the concentrated culture media Fig. 3, lanes 6–10. Interest-
Fig. 4. Size-exclusion chromatography of the secreted MFG-E8. Culture supernatants of MFG-E8-L (A), MFG-E8-S (B), DC1 (C) and DC2 (D)
transfectants were concentrated and applied to a Sephacryl S-300 column. Each fraction was monitored by ELISA using the antiserum specific for
MFG-E8. The peak positions of blue dextran (V
0
) and ovalbumin (43 kDa) are indicated with arrowheads. Each fraction was analyzed by Western
blotting with the antiserum specific for MFG-E8 (lower panels).
Fig. 3. Western blot analyses for cell surface and secreted MFG-E8.
COS-7 cells were transfected with plasmids containing MFG-E8-L
(lanes 2, 7 and 12), MFG-E8-S (lanes 3, 8 and 13), DC1 (lanes 4, 9 and
14) and DC2 (lanes 5, 10 and 15) or empty plasmid (lanes 1, 6 and 11).
Transfected COS-7 cells were cultured in serum-free medium
(DMEM) for 24 h. The cells were subjected to cell surface labeling with
sulfo-NHS-biotin and then lysed with the lysis buffer containing 1%
Triton X-100. Biotinylated proteins were precipitated with Streptavi-
din–Sepharose. The media were collected and concentrated by centri-
fugal filtration. Streptavidin-precipitates (lanes 1–5), the concentrated
media (lanes 6–10) and the total cell lysates (lanes 11–15) were analyzed
by SDS/PAGE followed by Western blotting with the antiserum spe-
cific for MFG-E8. Note that only MFG-E8-L (lane 2) and MFG-E8-S
(lane 3) were biotinylated, whereas all of the MFG-E8 and its mutants
were expressed and secreted (lanes 6–15). Positions of molecular-mass
standards are indicated on the right.
ÓFEBS 2002 MFG-E8: a component of secreted membrane vesicles (Eur. J. Biochem. 269) 1213


























