SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT
SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT
Two Alignment
Two Alignment
Multiple Alignment
Multiple Alignment

Fundamental
Fundamental
steps of the
steps of the
procedure
procedure
leading
leading
to optimal 2
to optimal 2
sequences
sequences
alignment
alignment
1
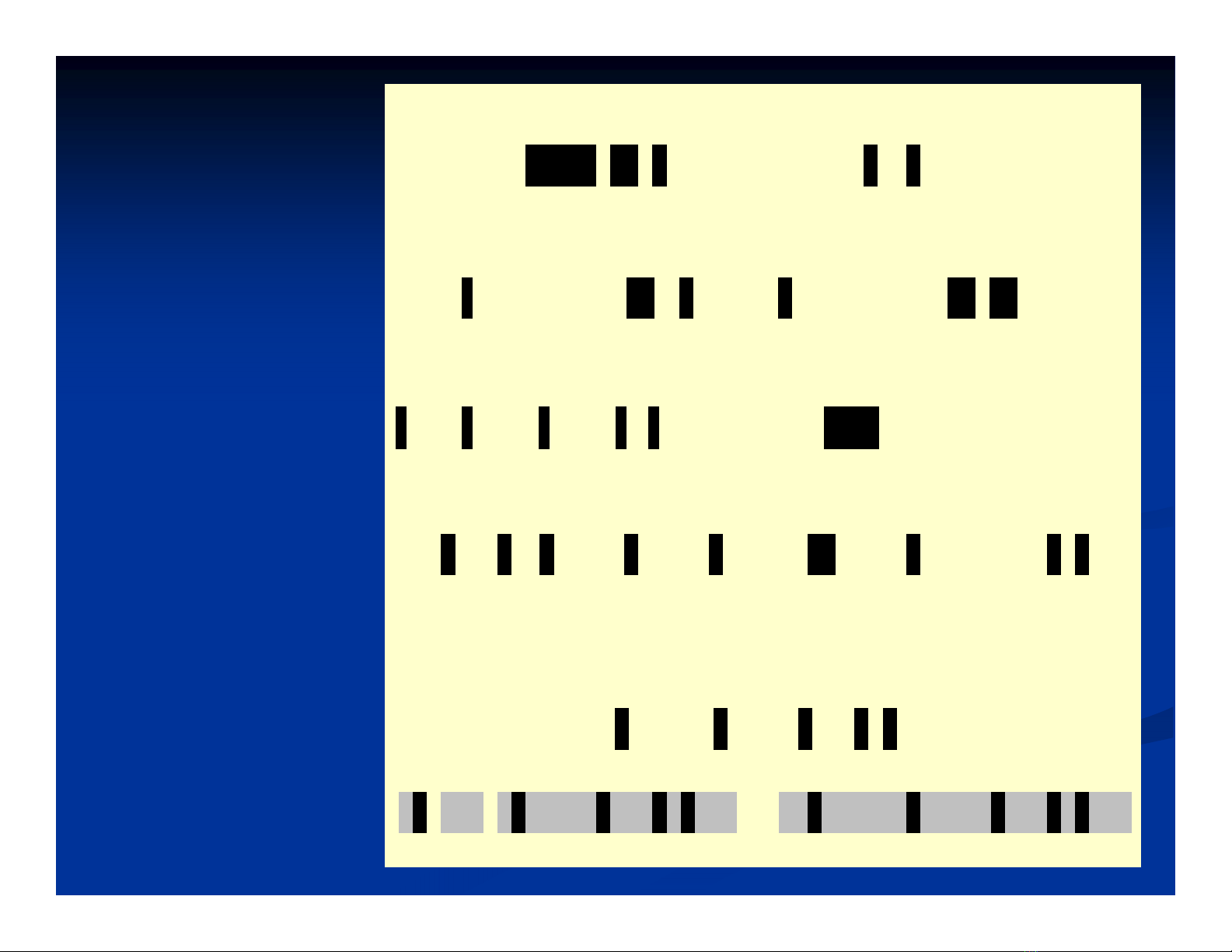
R V C P K I L M E C K K D S D C L A E C I C L E H G Y C G 0
M V C P K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D I G Y C G V S 0.0%
2
R V C P K I L M E C K K D S D C L A E C I C L E H G Y C G 0
M V C P K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D I G Y C G V S 0.0%
3
R V C P K I L M E C K K D S D C L A E C I C L E H G Y C G 0
M V C P K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D I G Y C G V S 0.0%
4
RVCPKILMECKKDSDCLAECICLEHGYCG 1
MVCP K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D I G Y C G V S 25.0%
5
R V C P K I L M E C K K D S D C L A E C I C L E H G Y C G 0
M V C P K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D I G Y C G V S 0.0%
•
•
•
n - 1
RVCPKILMECKKD S D C L A E C I C L E H G Y C G 1
MVCPKILMKCKH D S D C L L D C V C L E D I G Y C G V S 3.6%
n
RV C P K I L M EC K KDSDCLA E CIC L E H G Y C G 18
MV C P K I L M KC K HDSDCLL D CVC L E D I G Y C G V S 62.1%
n + 1
RVCPKILMECKKDSDCLA E C I C L E H G Y C G 5
MVCPKILMKCKHDSDCLLD C V C L E D I G Y C G V S 17.2%
n + 2
RVCPKILMECKKDS D C L A E CI C L E H G Y C G 2
MVCPKILMKCKHDSDC L L D C V CL E D I G Y C G V S 6.9%
•
•
•
n + m -3
R VCPKILMECKKDSDCLAECICLEHGYCG 1
M V C P K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D I G Y C G VS 33.3%
n + m -2
R V C P K I L M E C K K D S D C L A E C I C L E H G Y C G 0
M V C P K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D I G Y C G V S 0.0%
n + m -1
R V C P K I L M E C K K D S D C L A E C I C L E H G Y C G 0
M V C P K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D I G Y C G V S 0.0%
n
RVCPKILMEC K KD S D C L A E CIC L E H - G Y C G 22
MVCPKILMKC K HD S D C L L D CVC L E D I G Y C G V S 7 3 %
m

Comparison of
Comparison of
the fragments
the fragments
of 1st and 2nd
of 1st and 2nd
domain of
domain of
chicken
chicken
ovomucoid
ovomucoid
using unitary
using unitary
matrix, GCM,
matrix, GCM,
PAM250 and
PAM250 and
algorithm of
algorithm of
genetic
genetic
semihomology
semihomology
GTTAATTGCAGCCTGTATGCCAGCGGCATCGGCAAGGATGGGACGAGTTGGGTAGCC
1) V N C S L Y A S G I G K D G T S W V A
ATTGATTGCTCTCCGTACCTCCAA GTTGTAAGAGATGGTAACACCATGGTAGCC
2) I D C S P Y L Q - V V R D G N T M V A
V N C S L Y A S G I G K D G T S W V A %
I D C S P Y D G N T M V A
0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 7/19 36.8
GTTAATTGCAGCCTGTATGCCAGCGGCATCGGCAAGGATGGGACGAGTTGGGTAGCC
ATTGATTGCTCTCCGTACCTC GTTGTAAGAGATGGTAACACCATGGTAGCC
2 2 3 0 2 2 1 0 0 1 1 1 3 2 1 1 1 3 3 29/57 50.9
V N C S L Y A S G I G K D G T S W V A
42/97 43.3
I D C S P Y L V V R D G N T M V A
42/89 47.2
1 1 2 2 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 2 2 1 1 0 2 2 20/38 52.6
V N C S L Y A S G I G K D G T S W V A
I D C S P Y L V V R D G N T M V A
2 2 3 3 2 3 0 0 0 2 1 2 3 3 1 1 0 3 3 34/57 59.6
<L Q V V R>
< CAA >
< Q >
< Q >
UNITARY MATRIX
GENETIC CODE MATRIX
PAM250 SCORING
GENETIC SEMIHOMOLOGY
SCORE
What is
What is
important
important
in the
in the
protein
protein
similarity
similarity
search ?
search ?
1) Contribution (%) of identical positions
PKILMEC K KD 8 P K I LM E CK K D 2
PKILMKC K HD 8 0 % SDCLL D CV C L 2 0 %
similar not similar
2) Length of the compared strings (sequences)
LCE 1 M V EI CI E P K I RCI K V C T K D E R I T C L IL D ET 8
WCG 33.3% M V Y WCP R R F M HCV H L K A G G C T C W C L RL D Y Y 2 6 %
casual probably similar
3) Distribution of the identical positions along the analyzed sequence
MVEMICIEPKIRCIKVCTKDERITL 5 MVEMIMAGDARCIKVCTKDERITCL 5
HVYYWRPERFMHTVKLKAGGCRCWL 20% HHYYWMAGDAHTVQLKAGGCWCWAG 20%
casual similar
4) Residues at conservative positions
M V C P KI L M KC K HD S D C L LD C V C L ED M V C P K I L M K CK H D S D T L L D CVCL E D
E D E G KR R T KR E HF K E S N LA A A F K EQ Q N C P G P R E W CF T T R M N D S S CACP Q T
not similar similar
5) Structural/genetic similarity of the amino acids at non-conservative
positions
Identity only
M V C P K IL M K C K H DS D C L L D CV C L E D
R L C R R LV K R C R K ET E C I V E CI C I D E
Structural Genetic
M V C P K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D M V C P K I L M K C K H D S D C L L D C V C L E D
R L C R R L V K R C R K E T E C I V E C I C I D E R L C R R L V K R C R K E T E C I V E C I C I D E
The
The
sequence
sequence
identity
identity
estimation
estimation
procedure
procedure
The probability of randomly occurred minimum
identity match (a is equal to declared or higher) is:
Where:
x
– the number of unit types in sequence (20
for proteins; 4 for NA)
n
– the sequence length (the number of
compared position pairs)
a
– the number of identical positions
( )( )
n
kn
k
n
ak
an
x
xxx
k
n
P
2
1
−
=
−
=
∑



![Bài giảng Kỹ thuật DNA và công nghệ sinh học [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2022/20220110/trollhunters/135x160/9101641828200.jpg)








![Giáo trình Vi sinh vật học môi trường Phần 1: [Thêm thông tin chi tiết nếu có để tối ưu SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251015/khanhchi0906/135x160/45461768548101.jpg)





![Bài giảng Sinh học đại cương: Sinh thái học [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250812/oursky02/135x160/99371768295754.jpg)



![Đề cương ôn tập cuối kì môn Sinh học tế bào [Năm học mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260106/hoang52006/135x160/1251767755234.jpg)

![Cẩm Nang An Toàn Sinh Học Phòng Xét Nghiệm (Ấn Bản 4) [Mới Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251225/tangtuy08/135x160/61761766722917.jpg)