Giới thiệu tài liệu
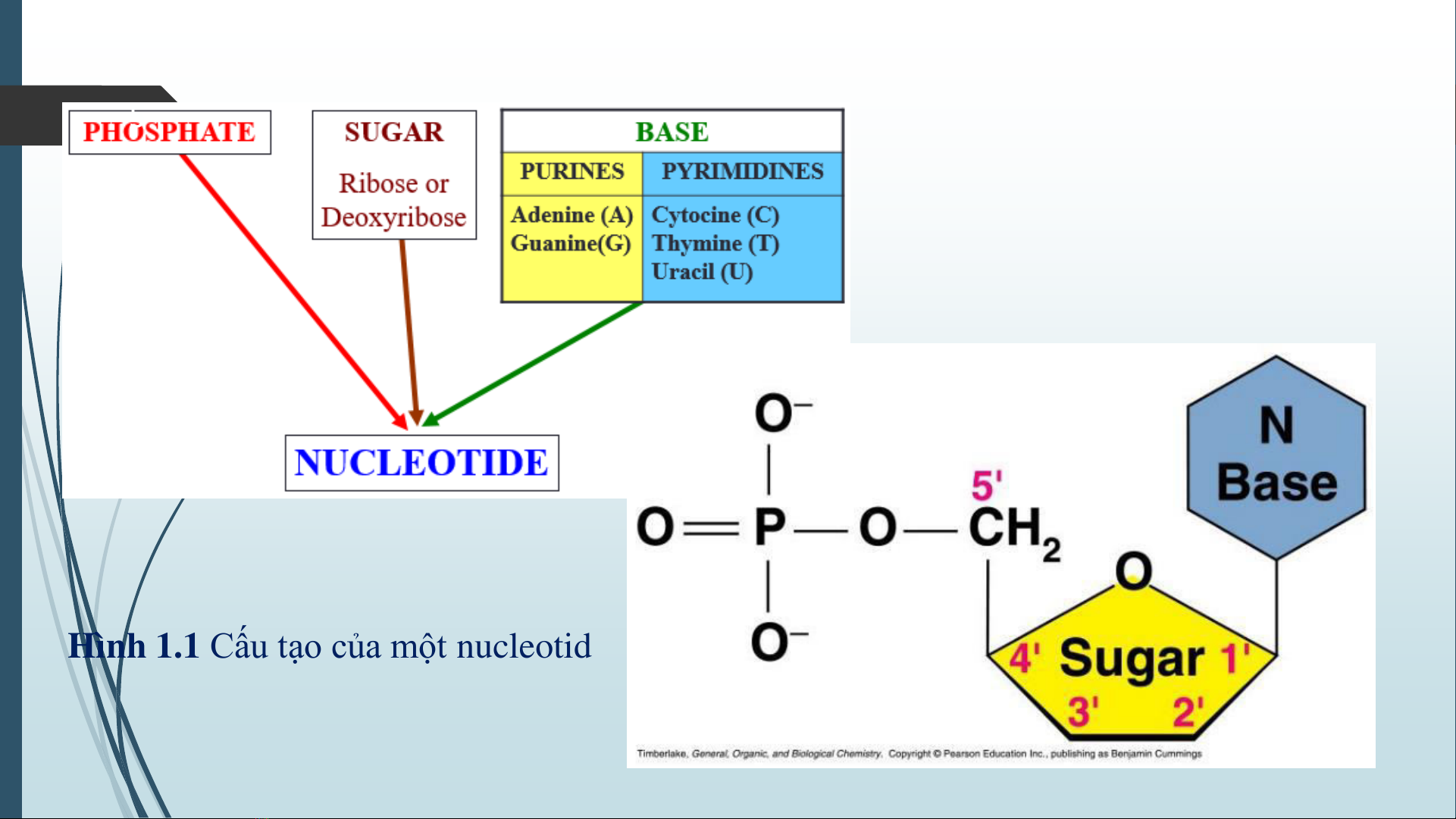
Chapter 1: Nucleic Acid introduces nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA. DNA is a double-stranded chain of nucleotides, each single strand forming a nucleotide chain. RNA is a single-stranded molecule with structure I and II. RNA is divided into several types, such as mRNA (messenger RNA), rRNA (ribosomal RNA) and tRNA (transfer RNA). The copying of DNA occurs according to the principle of base pair conservation, requiring a catalyst and reverse transcriptase enzyme. The transcription process creates an RNA supplemented with a strand of ADN. The protein synthesis machinery consists of four components: mRNA, tRNA, aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, and ribosome. The protein synthesis process occurs in the 5’ – 3’ direction, where the ribosome reads the code on mRNA and attaches an amino acid to the polypeptide chain.
Đối tượng sử dụng
This document is intended for biology students, researchers, and professionals working in the field of molecular biology.
Nội dung tóm tắt
Chapter 1: Nucleic Acid delves into the structure and function of nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, as well as the processes of DNA replication and protein synthesis. The chapter begins by describing the composition and structures of DNA and RNA molecules. DNA is a double helix formed from two single strands, each consisting of nucleotides. RNA exists in various forms, such as messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA). The chapter then explains the process of DNA replication through base pair conservation, requiring a catalyst and reverse transcriptase enzyme. This process creates an RNA strand complementary to one strand of the original DNA. Next, the chapter discusses protein synthesis, which occurs in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. The initiation phase involves the binding of mRNA to the small ribosomal subunit, followed by the attachment of the initiator tRNA and the assembly of the large ribosomal subunit. During the elongation phase, the ribosome moves along the mRNA strand and attaches successive amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain through a process called peptide bond formation. The termination phase occurs when the ribosome encounters a stop codon in the mRNA sequence, leading to the release of the completed polypeptide and the dissociation of the ribosomal subunits. Finally, the chapter highlights the importance of nucleic acids in various biological processes, such as gene expression and protein synthesis.



















![Bài giảng Giáp xác chân mái chèo [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250927/lethihongthuy2402@gmail.com/135x160/92891759114976.jpg)



![Tài liệu học tập Chuyên đề tế bào [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250906/huutuan0/135x160/56151757299182.jpg)






