INTERNAL MEDECINE JOURNAL OF VIETNAM|NO 22/2021
81
CLINICAL RESEARCH
APPLICATION OF NEURAL NETWORKS IN THE
DIAGNOSIS OF HEART DISEASE
Dao Thanh Tung1, Cao Vo San1
1Vietnam Military Medical University
ABSTRACT
Artificial neural networks, which are an essential tool in Machine Learning, are used to solve many types of
problems in different fields. This article will introduce an application of the artificial neural network model in
the diagnosis of heart disease based on the heart.csv data file. The results show that the built model has
high accuracy in the diagnosis, reaching 90.9%, and the area under the ROC curve is 0.939. Compared
with models built with ROC curves, logistic regression, decision trees, or discriminant analysis, the neural
network model proved superior in diagnosis.
* Keywords: Machine learning; Artificial neural networks; Prediction; Classification.
INTRODUCTION
In recent years, AI - Artificial Intelligence and more
specifically, Machine Learning has emerged as
evidence of the fourth industrial revolution.
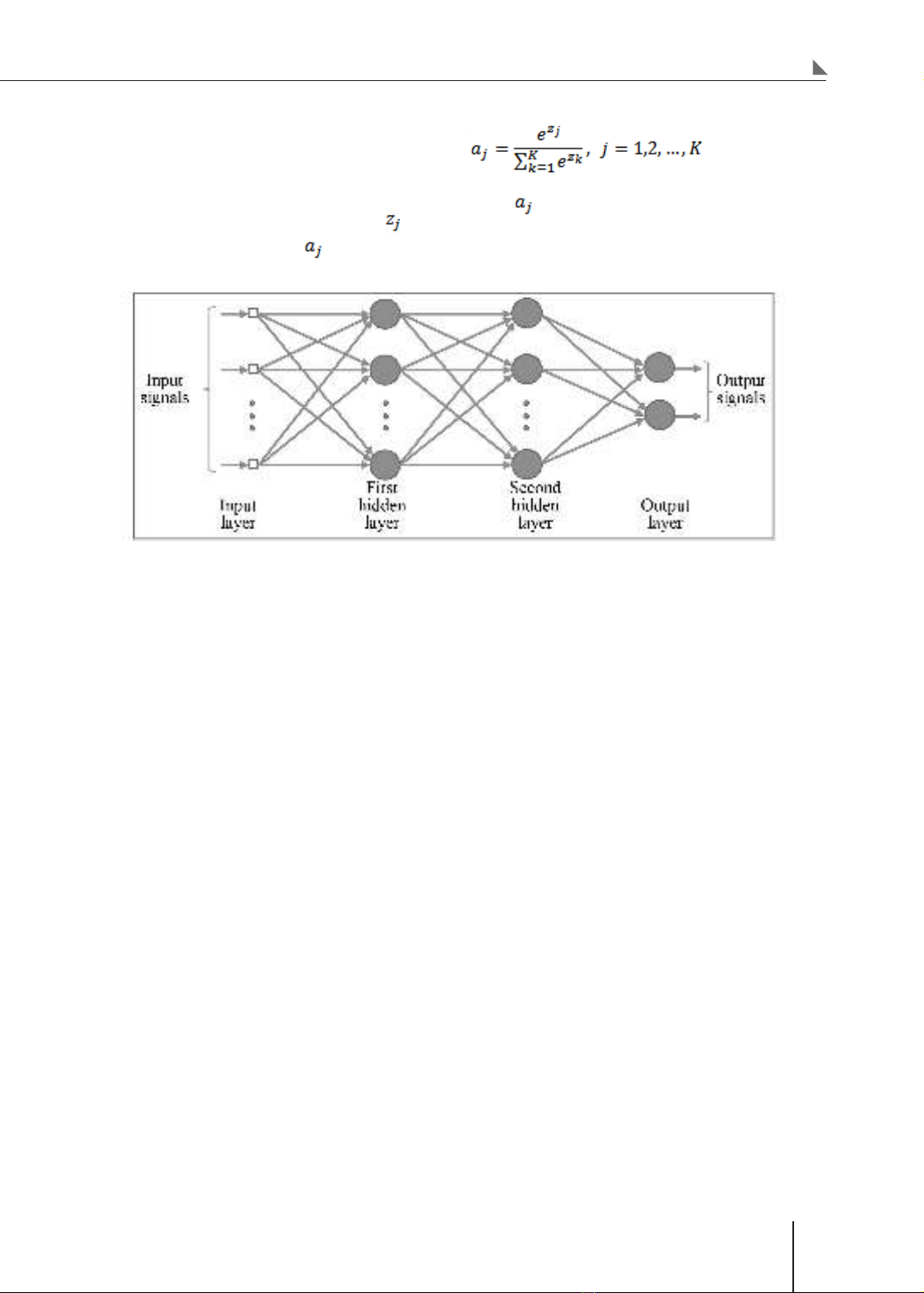
One of the models widely used in Machine
Learning is Artificial Neural Networks, in which the
Deep Learning technique proves its superiority
over traditional Machine Learning. In medicine,
many problems have been implemented by AI
applications, including the diagnosis of diseases.
The diagnosis is based on some clinical
information surveyed from a person, the doctor
who makes a diagnosis that he is sick or not. It
performs a classification that ranks a person into
one of the two layers (with disease: 1, no disease:
0). For diagnostic (forecast) or sorting objects,
we can build many models to guess data such as
ROC curve, logistic regression, decision tree, or
distinguished analysis, which helps the diagnosis
be effective. However, we always want to build a
model with the exact forecast rates as much as
possible that would replace people in diagnosis
and automatic prognosis.
In this article, the artificial neural network model
app. was used to diagnose a person with heart
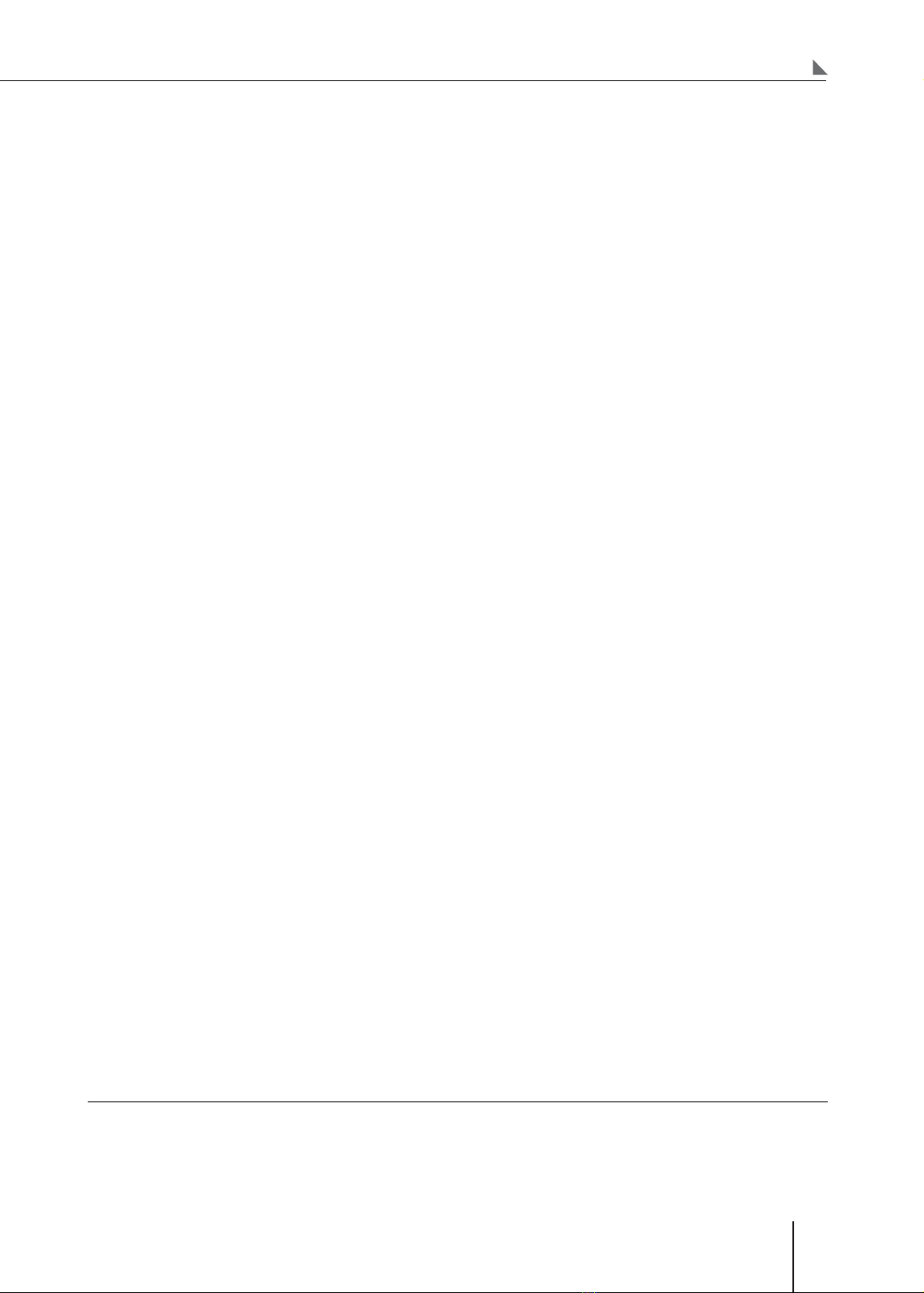
disease or not through the heart.csv data set [3]
of 303 people, including 165 sick people and 138
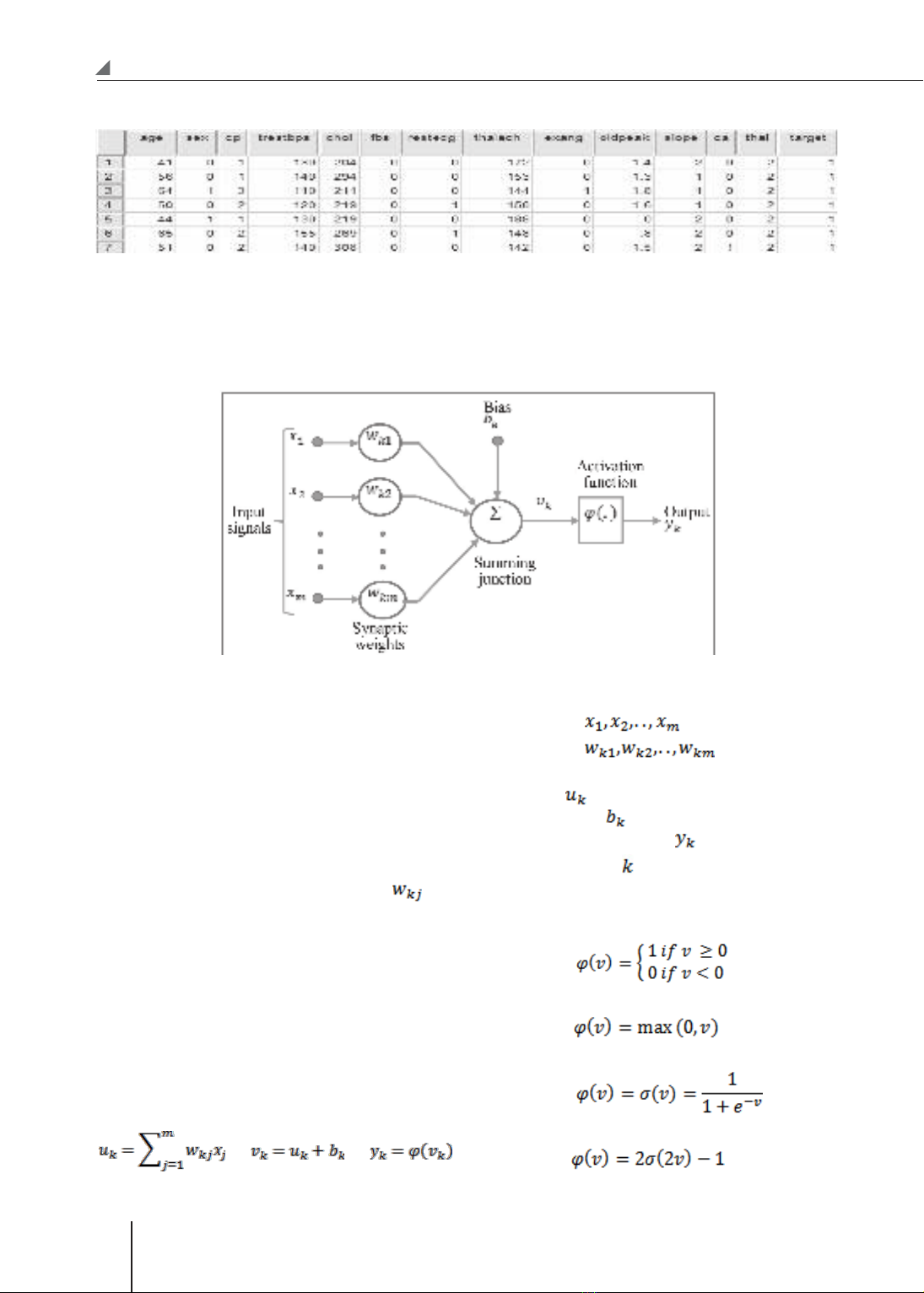
healthy people. This data set includes 14 variables:
age (age in years), sex (gender), cp (chest pain
type), trestbps (resting blood pressure (in mmHg on
admission to the hospital), chol (serum cholestoral
in mg/dl), fbs (fasting blood sugar > 120 mg/dl),
restecg (resting electrocardiographic results),
thalach (maximum heartbeat with Thallium Stress
Test), exang (exercise induced angina), oldpeak
(ST depression induced by exercise relative to
rest), slope (the slope of the peak exercise ST
segment), ca (number of major vessels (0-3)
colored by fluoroscopy) , thal (radioactive Thallium
test results) and target (have a disease or not).
Corresponding author: Dao Thanh Tung (daothanhtungk80@gmail.com)
Date received: 10/5/2021
Date accepted: 16/6/2021