TNU Journal of Science and Technology
230(05): 19 - 27
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 19 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
INHIBITORY ACTIVITY AGAINST Colletotrichum sp. CAUSES
ANTHRACNOSE DISEASE IN POST-HARVEST CHILI PEPPERS FROM
SOME PLANT EXTRACTS
Quach Van Cao Thi*, Nguyen Trung Truc
Vinh Long University of Technology Education
ARTICLE INFO
ABSTRACT
Received:
02/10/2024
Anthracnose is caused by Colletotrichum sp., causing significant
damage to the yield and quality of post-harvest chili peppers.
Therefore, the study was conducted to evaluate the antifungal activity
of plant extracts against Colletotrichum sp. under in vitro conditions.
The study isolated six strains of Colletotrichum sp. from chili peppers
infected with anthracnose in Vinh Long province. Chili peppers after
artificial infection exhibited disease symptoms similar to those of
natural anthracnose-infected chili peppers, of which strain OT1 had the
highest pathogenicity. Gene sequencing results showed that strain OT1
is 99.70% similar to Colletotrichum species on GenBank. Under in
vitro conditions, the inhibitory effect of plant extracts showed that all
extract treatments had inhibitory effects compared to the control
treatment (p < 0.05). The ethanol solvent extracts of moringa leaf
(Moringa oleifera Lam.) and Polyscias fruticosa exhibited the highest
inhibition efficiency, with the inhibition efficiency at 10 days after
treatment being 38.50% and 35.85%, respectively. The findings show
that plant extracts have a high potential for application in combination
with edible coatings to preserve pos-harvest chili peppers.
Revised:
17/12/2024
Published:
18/12/2024
KEYWORDS
Anthracnose disease
Antifungal activity
Colletotrichum sp.
Pepper chili
Plant extract
HOẠT TÍNH ỨC CHẾ NẤM Colletotrichum sp. GÂY BỆNH THÁN THƯ TRÊN
TRÁI ỚT SỪNG SAU THU HOẠCH CỦA MỘT SỐ DỊCH TRÍCH THỰC VẬT
Quách Văn Cao Thi*, Nguyễn Trung Trực
Trường Đại học Sư phạm Kỹ thuật Vĩnh Long
THÔNG TIN BÀI BÁO
TÓM TẮT
Ngày nhận bài:
02/10/2024
Bệnh thán thư do nấm Colletotrichum sp. gây thiệt hại lớn đến năng
suất cũng như chất lượng trái ớt sau thu hoạch. Do đó, nghiên cứu
được thực hiện nhằm đánh giá hoạt tính ức chế nấm Colletotrichum
sp. của một số loại dịch trích từ thực vật. Nghiên cứu đã phân lập được
6 chủng nấm Colletotrichum sp. từ trái ớt sừng nhiễm bệnh thán thư ở
tỉnh Vĩnh Long. Trái ớt sau khi lây nhiễm nhân tạo có các dấu hiệu
bệnh tương tự ớt nhiễm bệnh thán thư ngoài tự nhiên, trong đó chủng
OT1 có khả năng gây bệnh cao nhất. Kết quả giải trình tự gen cho thấy
chủng OT1 tương đồng 99,70% với các loài nấm thuộc chi
Colletotrichum trên ngân hàng Gene. Kết quả thí nghiệm cho thấy tất
cả các nghiệm thức xử lý dịch trích từ thực vật đều có hiệu quả ức chế
nấm bệnh so với nghiệm thức đối chứng (p < 0,05). Dịch trích bằng
dung môi ethanol của lá chùm ngây (Moringa oleifera Lam.) và đinh
lăng (Polyscias fruticose) cho hiệu quả ức chế cao nhất với hiệu quả
ức chế ở thời điểm 10 ngày sau khi xử lý lần lượt là 38,50% và
35,85%. Kết quả nghiên cứu cho thấy dịch trích thực vật có tiềm năng
ứng dụng cao trong việc phối hợp với các loại màng bao ăn được
(edible coatings) để bảo quản trái ớt sau thu hoạch.
Ngày hoàn thiện:
17/12/2024
Ngày đăng:
18/12/2024
TỪ KHÓA
Bệnh thán thư
Hoạt tính ức chế nấm
Colletotrichum sp.
Ớt
Dịch trích thực vật
DOI: https://doi.org/10.34238/tnu-jst.11219
* Corresponding author. Email: thiqvc@vlute.edu.vn

TNU Journal of Science and Technology
230(05): 19 - 27
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 20 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
1. Giới thiệu
Cây ớt (Capsium annuum L.) là một loại rau quan trọng và hiện nay đã được trồng ở nhiều quốc
gia. Trên thế giới, báo cáo của Tridge (2019) cho thấy ớt có sản lượng khoảng 75 triệu tấn [1]. Ở
Việt Nam, cây ớt được trồng ở nhiều tỉnh, thành, từ miền Bắc tới miền Nam do hiệu quả kinh tế
cao của trái ớt. Cũng như nhiều cây trồng khác, nấm Colletotrichum sp. gây bệnh thán thư được
xem là một trong số các dịch hại nguy hiểm trên ớt [2]. Chi Colletotrichum sp. được liệt kê là nhóm
nấm gây bệnh thực vật quan trọng thứ tám trên thế giới [3]. Nấm bệnh có thể xảy ra cả trên ruộng
và ở giai đoạn sau thu hoạch gây bệnh nặng trên trái trong quá trình vận chuyển xa, bảo quản lạnh
dẫn đến thiệt hại về kinh tế [4]. Ở nhiệt độ 28oC, ẩm độ 95,7%, bệnh thán thư sẽ bộc phát rất nhanh
[5]. Đây là một trong những nguyên nhân chính làm cho ớt thối rữa sau thu hoạch. Ở vùng Đồng
bằng sông Cửu Long (ĐBSCL) thiệt hại do bệnh thán thư khá cao, tỷ lệ bệnh trên cây trồng trong
vườn có khi lên đến 60% [6]. Ở Bình Dương, kết quả nghiên cứu của Trần Ngọc Hùng và Nguyễn
Thị Liên Thương (2016) cho thấy bệnh thán thư trên cây ớt được xác định là do chủng nấm C.
acatatum và C. truncatum [7]. Nghiên cứu của Trần Minh Dũng và cộng sự (2018) cũng đã xác
định được 2 chủng C. capsici và C. gloeosporioides gây bệnh thán thư trên trái ớt cay tại huyện Củ
Chi, thành phố Hồ Chí Minh [8].
Do ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng của bệnh thán thư gây hại trên trái ớt sau thu hoạch, một số nỗ lực
đã được thực hiện để kiểm soát bệnh này. Đồng thời, những lo ngại của người tiêu dùng về việc sử
dụng thuốc diệt nấm tổng hợp dẫn tới sự phát sinh tính kháng của nấm Colletotrichum sp. và nhu
cầu về các phương pháp bảo quản an toàn hơn đã dẫn đến việc sử dụng thuốc diệt nấm tổng hợp
không còn được phép sử dụng để kiểm soát bệnh thán thư trên ớt sau thu hoạch. Xuất phát từ thực
tế trên, việc tìm kiếm các giải pháp mới để kiểm soát nấm Colletotrichum theo hướng an toàn sinh
học, chẳng hạn như các hoạt chất ức chế nấm từ thực vật đã được thực hiện. Các hoạt chất thực vật
đã được báo cáo là chất kháng nấm hiệu quả, đồng thời có khả năng phân hủy sinh học dễ dàng và
tác dụng thuận lợi cho sự phát triển của vật chủ [9]. Dịch trích của một số loài thực vật như thân rễ
nghệ (Curcuma longa Linn), gừng (Zingiber officinale Roscoe), tỏi (Allium sativum), riềng
(Alpinia galanga L. Willd), rau má (Centella asiatica L.), dương xỉ (Dicranopteris linearis), mướp
đắng (Momordica charantia L.) có hiệu quả đối kháng in vitro với nấm Colletotrichum sp. [10].
Do đó, nghiên cứu này được thực hiện nhằm đánh giá hiệu quả của một số loại dịch trích thực vật
đối với bệnh thán thư do nấm Colletotrichum sp. trên trái ớt sừng. Kết quả của nghiên cứu là cơ sở
khoa học cho việc ứng dụng các loại dịch trích bổ sung vào các loại màng bao ăn được (edible
coatings) để bảo quản trái ớt sau thu hoạch theo hướng an toàn sinh học.
2. Đối tượng và phương pháp nghiên cứu
2.1. Đối tượng nghiên cứu
Một số loại thực vật phổ biến ở ĐBSCL như lá tía tô, đinh lăng, diếp cá, chùm ngây và lá bạch
đàn được sử dụng làm nguồn nguyên liệu trong nghiên cứu này.
2.2. Phương pháp thu mẫu và phân lập nấm Colletotrichum
Mẫu ớt nhiễm bệnh thán thư sau thu hoạch được thu ở một số ruộng trồng ớt của huyện Long
Hồ, tỉnh Vĩnh Long. Trái ớt bệnh có các dấu hiệu như những đốm tròn nhỏ màu xanh đậm hơi lõm
xuống, một số vết bệnh lớn có hình bầu dục, màu vàng hoặc trắng xám và đen. Trái ớt nhiễm bệnh
được thu và vận chuyển về phòng thí nghiệm. Mẫu bệnh được rửa lần 1 bằng nước cất khử trùng,
sau đó lau sạch bằng cồn 70o. Mẫu bệnh được cắt thành từng khoanh vuông có cạnh 1 – 3 mm,
gồm phần ranh giới giữa mô bệnh và mô khoẻ. Sau đó, mẫu được ngâm vào nước javen 1% và rửa
lại bằng nước cất khử trùng lần 2. Tiếp theo, mẫu bệnh được đặt trên môi trường PDA và ủ ở 28oC
± 2. Chủng nấm sau khi làm thuần được định danh sơ bộ bằng cách quan sát các đặc điểm hình thái
khuẩn ty và bào tử nấm bằng mắt thường và quan sát dưới kính hiển vi [11].

TNU Journal of Science and Technology
230(05): 19 - 27
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 21 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
2.3. Phương pháp xác định khả năng gây bệnh của các chủng nấm phân lập trên trái ớt
Khả năng gây bệnh của các chủng nấm phân lập được thực hiện theo Lê Thanh Toàn và cộng
sự (2020) [12]. Các bước lây nhiễm gồm: (1) Chuẩn bị dịch huyền phù: các chủng nấm thuần được
nuôi cấy trên môi trường PDA khoảng từ 5 – 7 ngày. Hút 5 ml nước cất tiệt trùng cho vào đĩa Petri
chứa nấm Colletotrichum sp. thuần. Sử dụng que cấy đã tiệt trùng cào nhẹ phần sợi nấm, lọc qua
giấy lọc và thu bào tử nấm. Bào tử nấm được chuẩn bị ở mật số 105 CFU/mL; (2) Chọn những trái
ớt không có dấu hiệu bị bệnh, không bị tổn thương về mặt cơ học, đồng đều về màu sắc và kích
thước. Mẫu được rửa sạch dưới vòi nước và được rửa thêm 2 lần nước cất tiệt trùng và để khô tự
nhiên ở nhiệt độ phòng; (3) Mẫu được lựa chọn, dùng kim châm tạo vết thương trên 3 vị trí ở vỏ
trái (độ sâu khoảng 1 mm); (4) Dịch huyền phù nấm được phun lên vết thương vừa tạo và để ráo;
(5) Cuối cùng, trái ớt sau khi lây nhiễm được ủ ở 25oC. Mỗi nghiệm thức (NT) được lặp lại 3 lần,
trong đó NT đối chứng được thay thế bằng nước cất tiệt trùng. Sự phát triển vết bệnh và triệu chứng
bệnh được ghi nhận ở ngày 2, 4, 6 và 8 sau lây nhiễm (NSLN).
2.4. Phương pháp định danh nấm Colletotrichum sp. bằng kỹ thuật PCR
Sau khi lây nhiễm, chủng nấm OT1 được định danh bằng phương pháp giải trình tự vùng ITS
(internal transcribed spacer). Nấm bệnh được ly trích DNA dựa theo phương pháp của Trần Nhân
Dũng và cộng sự (2012) [13]. Sau đó, vùng ITS của nấm bệnh được khuếch đại bằng PCR với cặp
mồi ITS1: 5’-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3’ và ITS4: 5′-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3′
[14]. Phản ứng PCR được thực hiện với thể tích là 25 μL, bao gồm: nước cất hai lần (BiH2O); PCR
Buffer (10X); dNTPs (200 µM); MgCl2 (1,5 mM); Taq DNA polymerase (2,5 UI); DNA mẫu (40
ng); mồi ITS1 (20 pmol) và mồi ITS4 (20 pmol). Sản phẩm PCR (600 bp) được điện di trên gel
agarose 1,5% và gửi Công ty TNHH DNA SEQUENCING (Thành phố Cần Thơ) để giải trình tự.
2.5. Phương pháp thu mẫu và tách chiết dịch trích thực vật
Lá tía tô (Perilla frutescens), lá đinh lăng (Polyscias fruticosa), lá diếp cá (Houttuynia cordata),
lá chùm ngây (Moringa oleifera) và lá bạch đàn (Eucalyptus citriodora) sử dụng trong các thí
nghiệm được thu hái tại huyện Long Hồ, tỉnh Vĩnh Long. Nguyên liệu lá thu hái vào thời điểm lúc
cây ra hoa, không sâu bệnh, trong điều kiện khô ráo và lá không dập nát.
Phương pháp điều chế cao chiết ethanol được thực hiện theo Basri và cộng sự (2005) nhưng có
một số thay đổi [15]. Nguyên liệu tươi sau khi thu hái được rửa với nước máy và để khô tự nhiên.
Mẫu được sấy ở 45ºC đến khối lượng không đổi. Mẫu sau đó được nghiền mịn và sàng qua rây có
d = 0,2 cm. Mẫu được trích ly với dung môi ethanol 99,7% (w/w) bằng phương pháp ngâm chiết
với tỷ lệ nguyên liệu/dung môi 1/10 (w/v) trong 24 giờ, lặp lại từ 3 – 5 lần cho đến khi dịch trích
trong. Sau cùng, dịch trích được loại bỏ dung môi bằng thiết bị cô quay chân không ở nhiệt độ
45oC và tốc độ quay 100 rpm. Dịch trích thu được sẽ được bảo quản ở nhiệt độ 4oC. Hiệu suất chiết
xuất (%) được xác định theo Turker và cộng sự (2009) như sau: Hiệu suất = khối lượng chất chiết
xuất (g)/khối lượng mẫu bột khô (g) *100 [16].
2.6. Khảo sát hiệu quả ức chế nấm bệnh của các loại dịch trích thực vật
Các khối nấm phân lập (đường kính 7 mm) cắt từ đĩa nấm thuần (sau 5 ngày nuôi cấy) được
chuyển vào trung tâm của đĩa môi trường PDA sau khi bổ sung dịch trích ở nồng độ 100 mg/mL
(được pha loãng trong DMSO 1%). Các đĩa Petri thí nghiệm được ủ ở nhiệt độ 28oC ± 2 trong 48
giờ. Mỗi NT được lặp lại 3 lần. Tản nấm được đo đường kính sau thời gian ủ là 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 ngày.
Hiệu quả ức chế của dịch trích với sự phát triển của vi nấm (%) được tính theo công thức của Tyagi
và cộng sự (2010) [17]: H (%) = [(R-r)/R] x 100, trong đó: R: đường kính nấm ở mẫu đối chứng
(cm), r: đường kính nấm ở mẫu có bổ sung dịch trích (cm).
2.7. Phương pháp xử lý số liệu

TNU Journal of Science and Technology
230(05): 19 - 27
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 22 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
Các đồ thị và số liệu thống kê mô tả được xử lý bằng phần mềm Excel 2016. Sự khác biệt giữa các
NT (p < 0,05) được phân tích phương sai (ANOVA) một nhân tố (kiểm định Turkey và độ tin cậy 95%)
bằng phần mềm Minitab 18. Công cụ BLASTn được sử dụng để so sánh sự tương đồng giữa vùng gen
ITS của chủng nấm Colletotrichum phân lập được với các trình tự trong ngân hàng Gene.
3. Kết quả và bàn luận
3.1.
Kết quả phân lập nấm Colletotrichum sp.
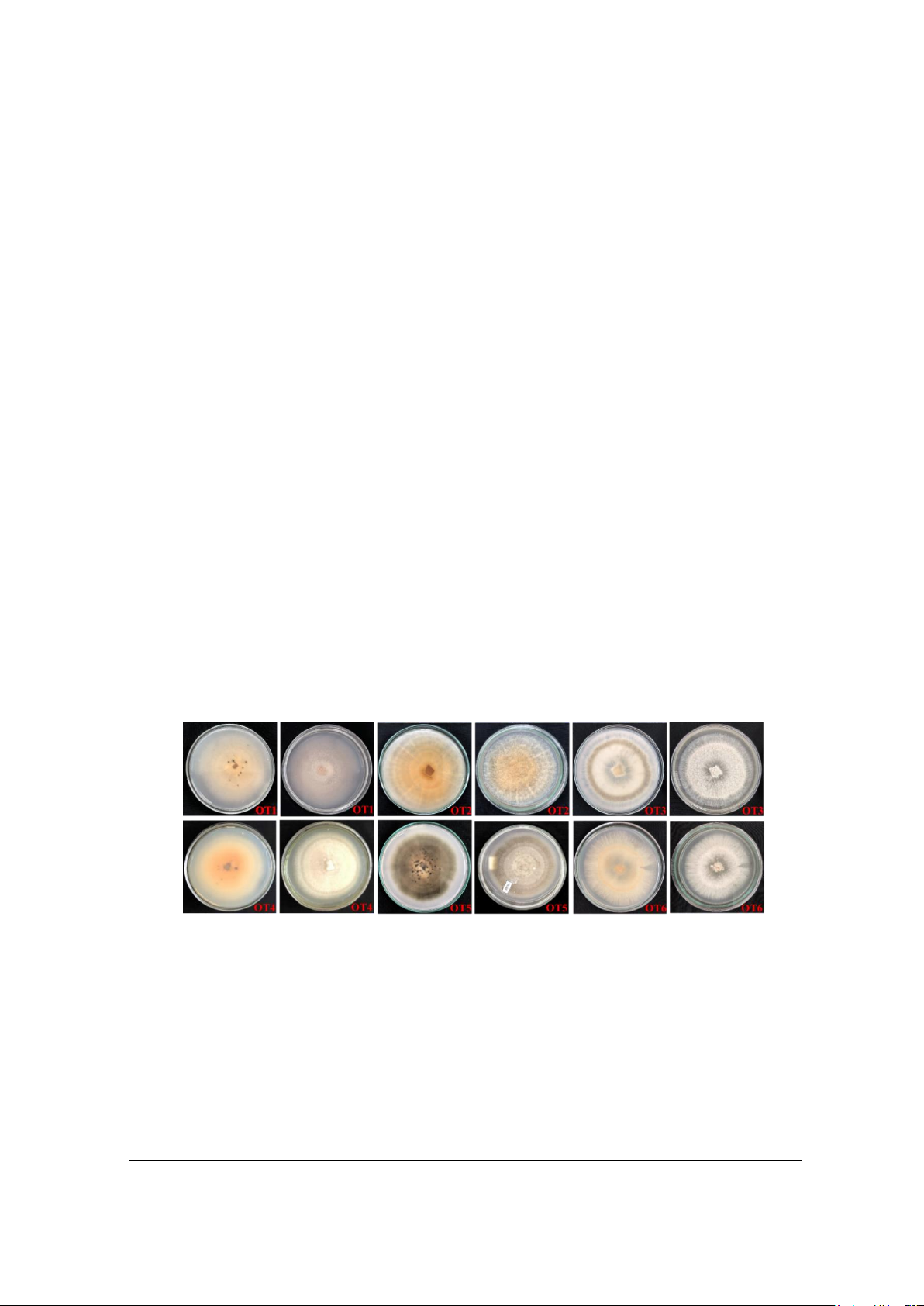
Từ các mẫu ớt bệnh thu thập, nghiên cứu đã phân lập được 6 chủng trên môi trường PDA. Các
chủng nấm phân lập được có đặc điểm tương đối đa dạng (Hình 1). Sau 5 – 7 ngày nuôi cấy ở nhiệt
độ 28oC, các mẫu cấy phát triển hình thành các vòng tròn từ trung tâm tản nấm. Kết quả quan sát cho
thấy tản nấm có màu cam, trắng hoặc hồng nhạt và chuyển sang màu xám xanh hoặc xám nhạt. Các
chủng OT1, OT2 và OT4 khuẩn lạc mọc tròn đều, phần mọc lên lúc đầu có màu cam nhạt hay cam
trắng. Sau 5 ngày nuôi cấy, đạt kích thước 45 – 55 mm, khi già tạo vòng tròn đồng tâm có màu cam
đến nâu đậm, sợi nấm có màu trắng nằm nhô lên trên, mọc dày đặc như bông. Trong khi chủng OT6
có khuẩn ty màu trắng vòng tròn đồng tâm có màu cam đậm, sau 5 ngày nuôi cấy chủng OT6 mọc
không đều, mép khuẩn lạc lượn sóng. Các chấm này là các đĩa cành tập trung một số lượng lớn bào
tử của nấm. Chủng OT5, khuẩn lạc có màu đen không liên tục, mọc kéo dài từ tâm ra. Trong khi
chủng OT3 có màu trắng đục vòng tròn đồng tâm màu xám, tơ dạng bông xốp, phát triển đều từ tâm
sau 5 ngày nuôi cấy. Nhìn chung, các chủng nấm phân lập có đặc điểm tương tự nấm Colletotrichum
đã báo cáo trước đây. Nghiên cứu của Oo và cộng sự (2017) [18] cho thấy sợi nấm Colletotrichum
phân lập từ trái ớt bệnh thán thư ở Hàn Quốc có màu xám nhạt đến màu cam nhạt.
Hình dạng bào tử nấm Colletotrichum sp. quan sát dưới kính hiển vi tương tự với những mô tả
trước đó của Oo và cộng sự (2017) [18], bào tử có dạng hình trụ, có vách ngăn với một đầu tròn,
một đầu nhọn hoặc cả hai đầu nhọn, có giọt dầu ở giữa tâm bào tử. Riêng bào tử của chủng OT2
có hình cong lưỡi liềm, hơi cong, đầu nhọn, bào tử không màu, vách trơn. Kết quả quan sát bào tử
của chủng OT2 dưới kính hiển vi cũng tương tự với kết quả nghiên cứu của Đoàn Thị Lan Anh và
cộng sự (2019) [19], bào tử Colletotrichum sp. quan sát dưới kính hiển vi có hình lưỡi liềm và
không màu.
Hình 1. Các dạng tản nấm Colletotrichum sp. trên môi trường PDA (mặt sau và mặt trước)
phân lập được từ trái ớt bệnh tại huyện Long Hồ
3.2. Khả năng gây bệnh của các chủng nấm phân lập
Khả năng gây bệnh của 6 chủng nấm Colletotrichum sp. phân lập trên trái ớt sau thu hoạch được
xác định bằng phương pháp lây nhiễm nhân tạo. Chiều dài vết bệnh thán thư trên trái ớt được ghi
nhận tại các thời điểm 2, 4, 6 và 8 NSLN (Bảng 1). Kết quả cho thấy tất cả các NT thực hiện lây
nhiễm có 100% biểu hiện bệnh thán thư. Trong khi đó, NT đối chứng hoàn toàn không có biểu hiện
bệnh thán thư (p < 0,05).
Tại thời điểm 2 NSLN, trừ NT đối chứng, tất cả các NT còn lại bắt đầu xuất hiện vết bệnh trên
trái ớt. Ở NT OT1 có chiều dài vết bệnh trung bình là 0,36 cm, khác biệt có ý nghĩa thống kê so

TNU Journal of Science and Technology
230(05): 19 - 27
http://jst.tnu.edu.vn 23 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn
với các NT còn lại (p < 0,05). Vết bệnh xuất hiện cho thấy nấm Colletotrichum sp. đã tấn công vào
mô trái và gây hại, điều này cho thấy khi gay vết thuong co giới đã tạo các lỗ hở để nấm xam
nhiễm vào ký chủ mọt cách dễ dàng hon. Triệu chứng điển hình là các vết bệnh khô, lõm nhỏ và
màu đen xuất hiện trên bề mặt trái (Hình 2). Tại thời điểm 4 NSLN, NT đối chứng vẫn chưa có dấu
hiệu xuất hiện vết bệnh thán thư. Tuy nhiên, 6 chủng nấm đều có khả năng gây bệnh, chiều dài vết
bệnh dao động từ 0,12 – 0,82 cm, trong đó chủng OT1 là chủng nấm có khả năng gây bệnh cao
nhất và thấp nhất là chủng OT2, tại các vết nhiễm bắt đầu có sự xuất hiện các sợi nấm màu trắng
(Hình 2). Tại thời điểm tiếp theo (6 NSLN), chủng nấm OT1 vẫn thể hiện khả năng gây bệnh cao
nhất với chiều dài vết bệnh là 1,02 cm, tiếp theo là các chủng OT6, OT5, OT3, OT4 và OT2 với
chiều dài vết bệnh lần lượt là 0,52; 0,31; 0,29; 0,23 và 0,19 cm. Tại thời điểm 8 NSLN, chiều dài
vết bệnh tiếp tục tăng ở tất cả các NT, chủng OT1 tiếp tục thể hiện khả năng gây hại cao nhất với
chiều dài vết bệnh 1,43 cm, các sợi nấm trắng tiếp tục phát triển và bao phủ hầu hết vết bệnh. Ở
NT đối chứng hoàn toàn không xuất hiện vết bệnh qua tất cả các thời điểm khảo sát, điều này có
thể giải thích do thí nghiệm được bố trí trong điều kiện vô trùng nên cách ly nguồn bệnh xâm nhập
từ bên ngoài trong suốt quá trình thí nghiệm. Nhìn chung, kết quả lây nhiễm cho thấy các chủng
nấm được phân lập ở những địa điểm khác nhau có khả năng gây bệnh khác nhau. Đặc biệt, chủng
OT1 có khả năng gây bệnh cao nhất qua tất cả các thời điểm khảo sát, do đó chủng OT1 được chọn
để thực hiện cho các thí nghiệm tiếp theo (Hình 2).
Bảng 1. Khả năng gây bệnh của các chủng nấm phân lập trong điều kiện in vitro
NT
Chiều dài vết bệnh (cm) ở các ngày sau lây bệnh
2 NSLN
4 NSLN
6 NSLN
8 NSLN
OT1
0,36a0,12
0,820,11
1,02a0,10
1,43a0,14
OT2
0,1b0,05
0,12d0,04
0,19d0,06
0,33d0,09
OT3
0,13b0,05
0,21cd0,06
0,29cd0,11
0,42cd0,11
OT4
0,12b0,04
0,17d0,05
0,23cd0,05
0,37d0,09
OT5
0,14b0,05
0,28bc0,07
0,31c0,08
0,56bc0,10
OT6
0,17b0,07
0,38b0,10
0,52b0,10
0,63b0,14
Đối chứng
0,00c0,00
0,00e0,00
0,00e0,00
0,00e0,00
Ghi chú: Các giá trị trong bảng là trung bình của ba lần lặp lại ± độ lệch chuẩn. Trong cùng một cột, các
giá trị có ký tự theo sau giống nhau thì khác biệt không có ý nghĩa thống kê (p > 0,05).
Ngày 0
Ngày 2
Ngày 4
Ngày 6
Ngày 8
Hình 2. Khả năng gây bệnh của chủng OT1 qua 8 NSLN
3.3.
Kết quả định danh chủng nấm phân lập
Kết quả PCR cho thấy 6 chủng nấm phân lập trong nghiên cứu đều khuếch đại được vùng ITS
với kích thước là 600 bp (Hình 3). Vùng ITS của chủng OT1 được giải trình và cho kết quả tương
đồng 99,70% với các loài Colletotrichum trên ngân hàng Gene (Hình 4). Kết quả xây dựng cây phả
hệ (Hình 5) cho thấy chủng OT1 phân lập thuộc cùng nhóm với các loài Colletotrichum trên ngân
hàng như C. scovillei isolate C01026 (MT645272.1), C. nymphaeae strain CNUCC 469-3-1
(PP809335.1), C. acutatum isolate PC007 (MK212356.1), C. citri isolate Cent01MO
(KT582172.1), C. indonesiense isolate Y53 (MK304343.1), C. melonis isolate Col-225
(MH685247.1) và C. eriobotryae isolate WZ-886 (OP163582.1).












![Giáo trình Vi sinh vật học môi trường Phần 1: [Thêm thông tin chi tiết nếu có để tối ưu SEO]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251015/khanhchi0906/135x160/45461768548101.jpg)





![Bài giảng Sinh học đại cương: Sinh thái học [mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20250812/oursky02/135x160/99371768295754.jpg)



![Đề cương ôn tập cuối kì môn Sinh học tế bào [Năm học mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2026/20260106/hoang52006/135x160/1251767755234.jpg)

![Cẩm Nang An Toàn Sinh Học Phòng Xét Nghiệm (Ấn Bản 4) [Mới Nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251225/tangtuy08/135x160/61761766722917.jpg)