Ch ng 5: Chi n l c kinh doanh qu c ươ ế ượ ố
tế
I. Chi n l c toàn c uế ượ ầ
II. Xâm nh p th tr ng qu c t ậ ị ườ ố ế
III. Marketing toàn c uầ
IV. Đi u hành s n xu t toàn c u ề ả ấ ầ
V. Qu n tr ngu n nhân l c toàn c uả ị ồ ự ầ
I. Chi n l c toàn c uế ượ ầ
Chi n l c: ế ượ
“hành đ ng mà qu n tr gia ti n hành đ đ t ộ ả ị ế ể ạ
đ c m c tiêu c a công ty” ượ ụ ủ
M c tiêu chung: ụ
T i đa hóa l i ích/l i nhu nố ợ ợ ậ
Khác bi t hóa s n ph m; tăng giá bán thông qua vi c ệ ả ẩ ệ
gia tăng các giá tr , đ c tính s n ph m, ch t l ng, d ch ị ặ ả ẩ ấ ượ ị
v ụ
H th p chi phíạ ấ
Ph ng ti n : Phân b các ngu n l c h n ươ ệ ố ồ ự ạ
ch đ đ t m c tiêuế ể ạ ụ

Qu n tr chi n l c qu c t là gì?ả ị ế ượ ố ế
International strategic
management is a
comprehensive and ongoing
management planning process
aimed at formulating and
implementing strategies that
enable a firm to compete
effectively internationally
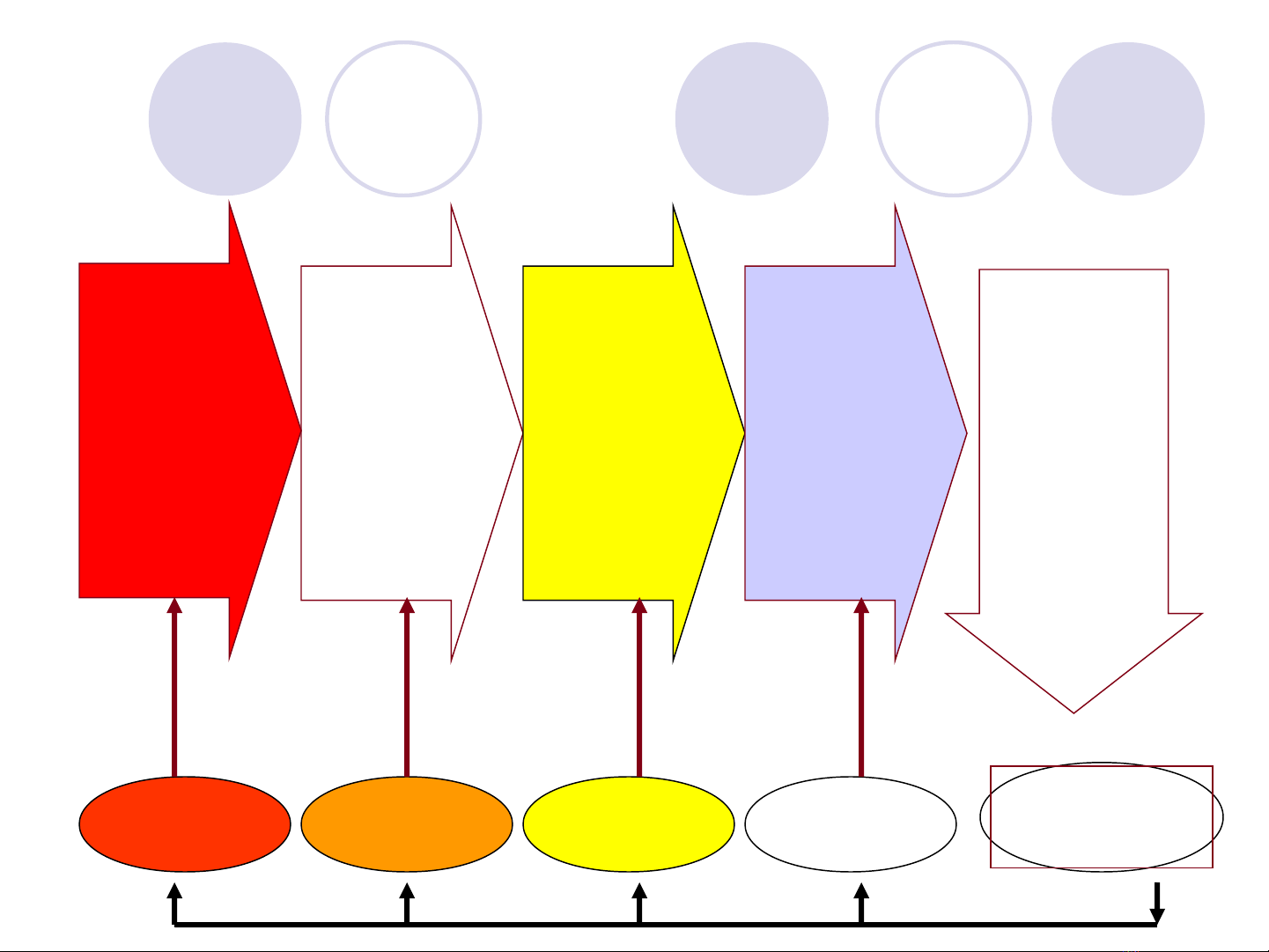
International strategic management process
Developing a
Strategic
Vision and
setting
Business
Objectives
Crafting an
international
Strategy to
Achieve the
Objectives, & fit
with
Environment
Implementing
and Executing
the Strategy
at Corporate/
Business/
Functional levels
Evaluating
performance,
Monitoring
New
Developments
and initiating
Corrective
Adjustments
Revise as
needed
Revise as
needed
Improve/
Change as
needed
Recycle to Tasks
1, 2, 3, or 4 as
Needed
Task 1 Task 2 Task 3 Task 4 Task 5
Analysing the
Internal and
External
Environments
S.T.E.P
»Analysis, formulation, implementation…
Improve/
Change as
needed
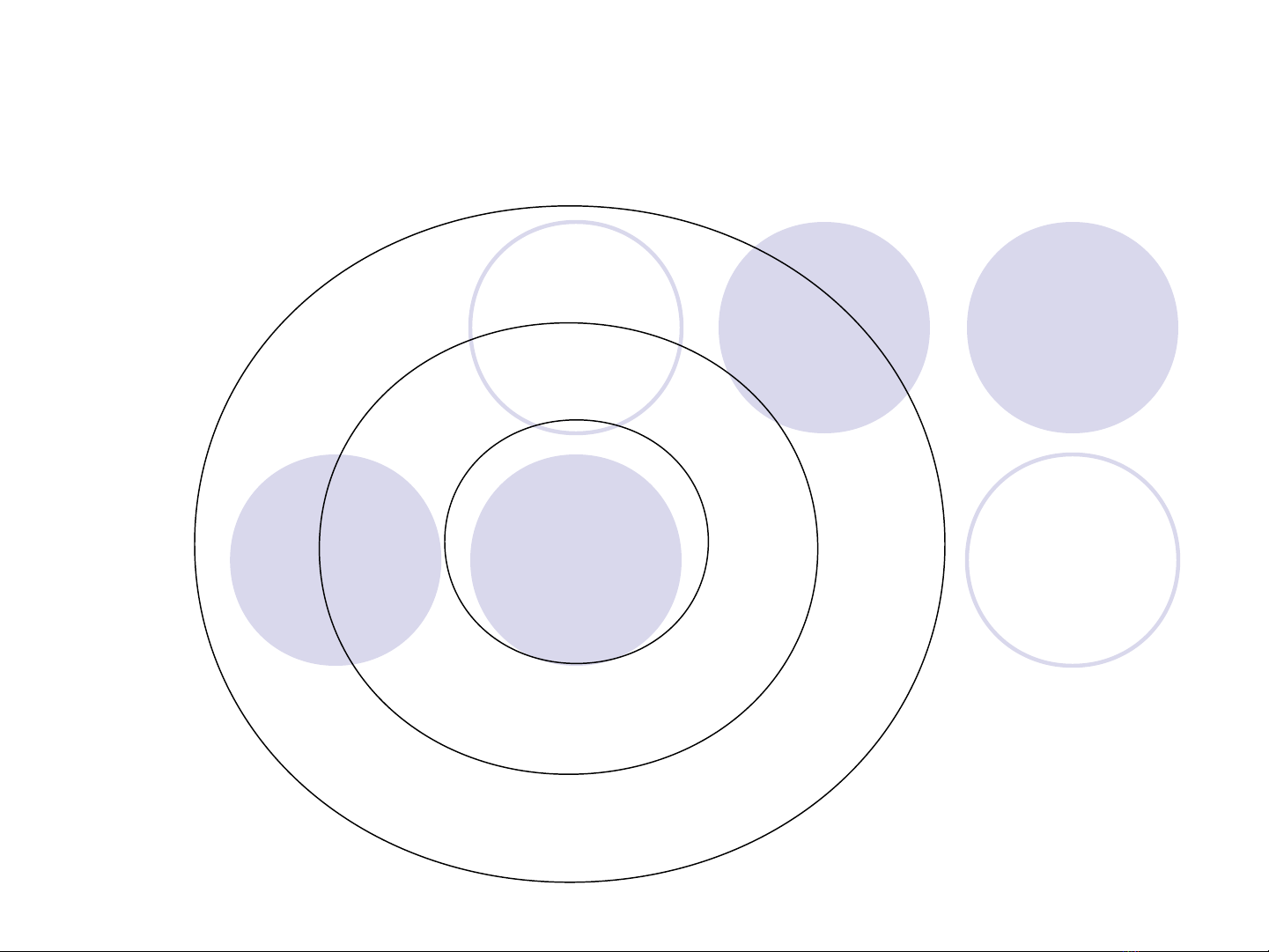
Environmental Analysis
External macro-
environment
External micro-
environment
Internal
environment
The industry and
supply chain
STEP influences
Analysis is the
critical
starting point
of strategic
thinking. –
Kenichi
Ohmae


























