Extra-pulmonary TB
-
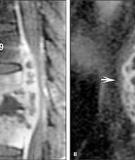
Pott disease is rare and responsible for only 1%–2% of all tuberculosis cases. It poses diagnostic challenges in resource-limited settings due to unusual presentation and limited investigative capacity, resulting in debilitating sequelae if diagnosed late.
 5p
5p  vitiki
vitiki
 30-01-2024
30-01-2024
 2
2
 2
2
 Download
Download
-
Urinary tract tuberculosis (UTTB) is a common form of extrapulmonary tuberculosis (TB) which can infrequently present as renal carcinoma, leading to serious errors in the diagnosis and treatment of UTTB.
 4p
4p  vigamora
vigamora
 23-05-2023
23-05-2023
 6
6
 2
2
 Download
Download
-
The accuracy of currently available same-day diagnostic tools (smear microscopy and conventional nucleic acid amplification tests) for pleural tuberculosis (TB) is sub-optimal. Newer technologies may offer improved detection.
 10p
10p  vimontana2711
vimontana2711
 05-04-2021
05-04-2021
 12
12
 2
2
 Download
Download
-
Little is known about the pathway to diagnosis of lymphoma in Sub-Saharan Africa, despite the increased risk of lymphoma in people living with HIV (PLHIV). The challenges of diagnosis in this setting include diagnostic confusion with extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB), which commonly causes lymphadenopathy in PLHIV.
 11p
11p  vikuala271
vikuala271
 13-06-2020
13-06-2020
 8
8
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
Tuberculosis (TB) is a major public health problem in India and a leading cause of death in adults, especially among the economically productive age group. Historically TB has been associated with significant morbidity and mortality and remains a major global health problem.
 11p
11p  nguaconbaynhay1
nguaconbaynhay1
 04-12-2019
04-12-2019
 50
50
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
Broad management of NTDs contributes towards enhanced cognitive and physical development and to the reduction in number of underweight, malnourished and stunted children under the nutrition and child health targets, as well as to improved maternal health. Reduction of worm burden can also lead to improved health outcomes for individuals suffering from HIV/AIDS, TB and malaria. The GOK considers integrated management and control of NTDs both attainable and a high priority.
 44p
44p  nhamnhiqa
nhamnhiqa
 01-03-2013
01-03-2013
 32
32
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
Maternal mortality levels in Kenya remain unacceptably high at 488 per 100,000 live births 1 . The United Nations estimated in 2005 that 1 in every 39 Kenyan women die in childbirth; while major progress has been made in reducing infant and child mortality rates, one in every 19 babies born in Kenya this year will die before their first birthday. 60% of these deaths will occur in the neonatal period.
 138p
138p  nhamnhiqa
nhamnhiqa
 01-03-2013
01-03-2013
 45
45
 3
3
 Download
Download
-
Members of the WHO Expert Group on Smear- Negative TB: Getachew Aderaye (Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia), Ludwig Apers (Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, Belgium), Leopold Blanc (World Health Organization, Switzerland), Amy Bloom (United States Agency for International Development, United States of America), Jermiah Chakaya (Ministry of Health, Kenya), Liz Corbett (London School of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, United Kingdom), Haileyesus Getahun (World Health Organization, Switzerland), Charlie Gilks (World Health Organization, Switzerland), Jeroen van Gorkom (KNCV Tuberculosis F...
 44p
44p  enter1cai
enter1cai
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 51
51
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
The infectiousness of a TB patient is directly related to the number of droplet nuclei carrying M. tuberculosis (tubercle bacilli) that are expelled into the air. Depending on the environment, these tiny particles can remain suspended in the air for several hours. M. tuberculosis is transmitted through the air, not by surface contact. Infection occurs when a person inhales droplet nuclei containing M. tuberculosis, and the droplet nuclei traverse the mouth or nasal passages, upper respiratory tract, and bronchi to reach the alveoli of the lungs.
 38p
38p  enter1cai
enter1cai
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 48
48
 5
5
 Download
Download
-
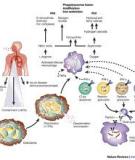
Extrapulmonary involvement can occur in isolation or along with a pulmonary focus as in the case of patients with disseminated tuberculosis (TB). The recent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) pandemic has resulted in changing epidemiology and has once again brought extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) into focus. EPTB constitutes about 15 to 20 per cent of all cases of tuberculosis in immunocompetent patients and accounts for more than 50 per cent of the cases in HIV-positive individuals.
 38p
38p  enter1cai
enter1cai
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 48
48
 2
2
 Download
Download
-
Extrapulmonary organ involvement in human immunodefiaency virus (HIV)-infected patients with pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is reported to be 26%, however, the clinical predictors of extrapulmonary involvement in pulmonary TB patients has not been reported yet. We tried to determine the clinical predictors of presence of extrapulmonary involvement in patients with pulmonary TB. Cross-sectional study was performed including all adult patients with culture-proven pulmonary TB diagnosed between January 1, 2004 and July 30, 2006, at a tertiary referral hospital in South Korea.
 5p
5p  taisaocothedung
taisaocothedung
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 47
47
 4
4
 Download
Download
CHỦ ĐỀ BẠN MUỐN TÌM