Sputum microscopy
-
Several studies have compared the diagnostic value of sputum induction (SI) with flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy (FOB) in diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis; however, these investigations yield an inconsistent conclusion. This study aims to evaluate the role of acid-fast bacilli (AFB) testing of SI and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) samples in suspected pulmonary tuberculosis cases.
 7p
7p  vikissinger
vikissinger
 21-12-2023
21-12-2023
 3
3
 2
2
 Download
Download
-
Xpert MTB/RIF has been shown to have a superior sensitivity to microscopy for acid fast bacilli (AFB) in sputum and has been recommended as a standard first line investigation for pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB). Bronchoscopy is a valuable tool in diagnosing PTB in sputum negative patients.
 5p
5p  vimontana2711
vimontana2711
 05-04-2021
05-04-2021
 11
11
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
Fiberoptic bronchoscopy (FOB) is a useful diagnosis tool in low-burden countries for patients with suspected pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) who are smear-negative or sputum-scarce. This study sought to determine the accuracy of the Xpert® MTB/RIF (XP) assay using FOB samples.
 7p
7p  vimontana2711
vimontana2711
 05-04-2021
05-04-2021
 16
16
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
During the study period (July to December 2016) a total of 188 samples (sputum and blood from each person) have been tested in the National Reference Laboratory (NRL) at the Institute of Chest and Respiratory Diseases / Baghdad. These cases are considered as suspected pulmonary tuberculosis. This study for these 188 suspected specimens declare that, 103 (54.78%) cases were positive using direct assay (AFB smear microscopy) and 85 (45.21%) were considered to be negative cases by smear microscopy.
 12p
12p  quenchua6
quenchua6
 15-06-2020
15-06-2020
 14
14
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
Tuberculosis (TB) still remains a global health problem affecting one third of world population. Early diagnosis of TB is very important for therapeutic reasons and to control the spread of infection. For developing countries with a large number of cases and financial constraints, evaluation of rapid and inexpensive diagnostic methods has a great importance.
 7p
7p  trinhthamhodang1213
trinhthamhodang1213
 29-05-2020
29-05-2020
 28
28
 0
0
 Download
Download
-
The bacteriological diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB) is largely dependent on the Ziehl-Neelsen (ZN) microscopy. This method has a low sensitivity, which can be improved by the concentration of the specimen with sodium hypochlorite or Bleach (NaOCl), followed by sedimentation after doing LED. This study was conducted to evaluate the efficiency of bleach sedimentation technique in detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by LED microscopy. A Total of 100 sputum samples from the patients who visited RNTCP of Rama Medical College Hospital and Research Centre between April 2015 and March 2016.
 7p
7p  trinhthamhodang5
trinhthamhodang5
 16-05-2020
16-05-2020
 8
8
 0
0
 Download
Download
-
Nowadays the technology has rapidly advanced in the detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis and drug susceptibility clinical sample. The examination that include the advances microscopic, in viro-culture and application in molecular base. In developing countries the world health organization is played a role for evaluating and developing the technology of their efficiency, feasibility at present in India, natural network and designed microbiology centre, and also intermediate reference laboratories implemented by the revised national tuberculosis control programme RNTCP.
 9p
9p  nguaconbaynhay5
nguaconbaynhay5
 11-05-2020
11-05-2020
 8
8
 0
0
 Download
Download
-
This study covering the period from January 2017 to June 2017 was conducted at Department of Microbiology, SN Medical College, India. A total of 300 patients suspecting of having tuberculosis and consenting for HIV testing were included in the study. The TB diagnosis was performed using sputum microscopy (AFB staining) and all the cases were screened for HIV by using rapid HIV kits according to NACO guidelines. Overall, 29 (9.66%) cases were diagnosed as sputum positive pulmonary tuberculosis among which 2 cases (6.90 %) were sero-positive for HIV antibodies.
 4p
4p  angicungduoc4
angicungduoc4
 04-05-2020
04-05-2020
 16
16
 0
0
 Download
Download
-
Bacteriological confirmation plays a key role in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Many systems have been developed in the recent years apart from traditional microscopy and culture on Lowenstein Jensen (LJ) medium. The objective of this study is to compare the rate of detection of Mycobacteria by acid fast staining, LJ medium and Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube (MGIT). Hundred patients with clinical suspicion of pulmonary tuberculosis attending a tertiary care hospital over a period of one and a half years were enrolled in the study.
 8p
8p  caygaocaolon4
caygaocaolon4
 01-04-2020
01-04-2020
 8
8
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
Tuberculosis (TB) is the commonest opportunistic infection and cause of death in patients with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) in developing countries. World Health Organization (WHO) recommends 85% treatment success rate for all TB cases as an indicator of TB control. The study aimed at determining TB co infection among the seropositive cases. It was a cross-sectional study among seropositive patients whose sociodemographic characteristics with treatment history were obtained using a semi-structured questionnaire.
 5p
5p  trinhthamhodang3
trinhthamhodang3
 14-02-2020
14-02-2020
 15
15
 0
0
 Download
Download
-
HIV and TB co-infection is an alarming situation in the health care system. India has the third largest number of people living with HIV (PLHIV) in the world. This co-infection leads to difficulty in both diagnosis and treatment of TB resulting in increased mortality, morbidity, treatment failure and relapse. The present study was conducted to determine the prevalence of TB in PLHIV and also to determine its co-relation with the CD4 counts of the affected individuals. This is a prospective study conducted over a period of one year commencing from April 2017 to March 2018.
 6p
6p  trinhthamhodang3
trinhthamhodang3
 12-02-2020
12-02-2020
 12
12
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
TB is the most common opportunistic infection (OI) among HIV infected individuals, and co infected individuals are at high risk of death. TB is the largest single cause of death in the setting of AIDS, accounting for 26% of AIDS related deaths, 99% of which occur in developing countries. HIV Associated Tuberculosis remains a major global public health challenge. Hence routine TB screening among PLWHA (People Living with HIV-AIDS) offers the opportunity to identify those without TB, helps for early diagnosis and promptly treat TB. The aims of the study are 1.
 6p
6p  kequaidan2
kequaidan2
 11-12-2019
11-12-2019
 7
7
 0
0
 Download
Download
-
An infectious case of pulmonary tuberculosis is diagnosed by demonstrating tubercle bacilli in sputum. The laboratory methods available for this purpose are sputum microscopy, isolation of tubercle bacilli in culture followed by identification of the bacilli and animal pathogenicity tests. Evidence based on all the three methods establishes bacteriological diagnosis beyond any doubt, but even economically advanced countries may not consider such an elaborate procedure essential for routine diagnosis.
 12p
12p  taisaocothedung
taisaocothedung
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 71
71
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
The Bangalore district tuberculosis programme (the programme assessed). The Bangalore District has an area of 7798 square kilometers and had a population of about 1.3 million according to the census of 1961 (excluding the metropolitan area). The District has 13 towns and 2477 villages. The DTP was implemented in 1963, not by the staff of the DTC (as happens in other districts) but by trainees of two courses held in 1963 at the National Tuberculosis Institute (NTI) Bangalore. In all, 15 microscopy centres were organised in general health institutions of the District.
 5p
5p  taisaocothedung
taisaocothedung
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 47
47
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
The sensitivity of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) makes it a potential diagnostic test for detection of M. tuberculosis in samples with low bacillary load. Aim: To assess the efficiency of PCR as compared to routine diagnostics in detection of M. tuberculosis from sputum samples of suspects referred to a tuberculosis clinic and those identified during a morbidity survey. Methods: Respiratory samples (sputum with or without saliva) from 144 individuals were examined by PCR, using MPB64 primers, culture and microscopy.
 8p
8p  taisaocothedung
taisaocothedung
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 64
64
 2
2
 Download
Download
-
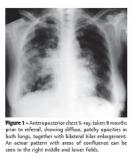
About a third of the world’s population is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis remains one of the biggest killers among infectious diseases, with up to three million people dying from tuberculosis each year (Dye 1999). Diagnosis of tuberculosis generally relies on smear microscopy and culture of the sputum. The disease typically results in progressively destructive lung lesions but may affect almost any part of the body, usually with advanced wasting and death inmore than half of cases in the absence of intervention.
 4p
4p  taisaocothedung
taisaocothedung
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 38
38
 2
2
 Download
Download
-
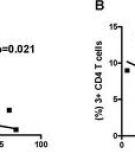
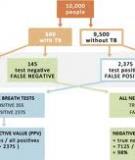
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in breath may contain biomarkers of active pulmonary tuberculosis derived from the infectious organism (metabolites of Mycobacterium tuberculosis) and from the infected host (products of oxidative stress). Methods: We analyzed breath VOCs in 226 symptomatic high-risk patients in USA, Philippines, and UK, using gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy. Diagnosis of disease was based on sputum culture, smear microscopy, chest radiography and clinical suspicion of tuberculosis (CSTB). Chromatograms were converted to a series of 8 s overlapping time slices.
 7p
7p  taisaocothedung
taisaocothedung
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 49
49
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
People concentrated in congregated systems, such as prisons, are important but often neglected reservoirs for TB transmission, and threaten those in the outside community. Therefore, this study was conducted to determine the prevalence of tuberculosis in a prison system of North Gondar Zone. Methods: An active case-finding survey in North Gondar Prison was carried out from March to May 2011. All prison inmates who had history of cough for at least a week were included in the study.
 7p
7p  taisaocothedung
taisaocothedung
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 41
41
 2
2
 Download
Download
-
Tanzania ranks 15th among the world’s 22 countries with the largest tuberculosis burden and tuberculosis has continued to be among the major public health problems in the country. Limited data, especially in patients co infected with HIV, are available to predict the duration of time required for a smear positive pulmonary tuberculosis patient to achieve sputum conversion after starting effective treatment.
 6p
6p  taisaocothedung
taisaocothedung
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 47
47
 1
1
 Download
Download
-
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) associated tuberculosis (TB) remains a major global public health challenge, with an estimated 1.4 million patients worldwide. Co-infection with HIV leads to challenges in both the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis. Further, there has been an increase in rates of drug resistant tuberculosis, including multi-drug (MDR-TB) and extensively drug resistant TB (XDRTB), which are difficult to treat and contribute to increased mortality.
 16p
16p  taisaocothedung
taisaocothedung
 12-01-2013
12-01-2013
 49
49
 1
1
 Download
Download
CHỦ ĐỀ BẠN MUỐN TÌM