An Toàn M ng:ạ
T ng l a (Firewall)ườ ử
Võ Vi t Minh Nh tế ậ
Khoa CNTT – Tr ng ĐHKHườ

N i dung trình bàyộ
Các khái ni m c b nệ ơ ả
Các ki u firewall khác nhauể
Packet filtering and stateless filtering
Stateful filtering
Deep packet layer inspection
Nâng cao kh năng cho firewallả
C ch chuy n đ i đ a chơ ế ể ổ ị ỉ
Các d ch v proxyị ụ
L c n i dungọ ộ
Ph n m m ch ng virusầ ề ố

Các khái ni m c b nệ ơ ả
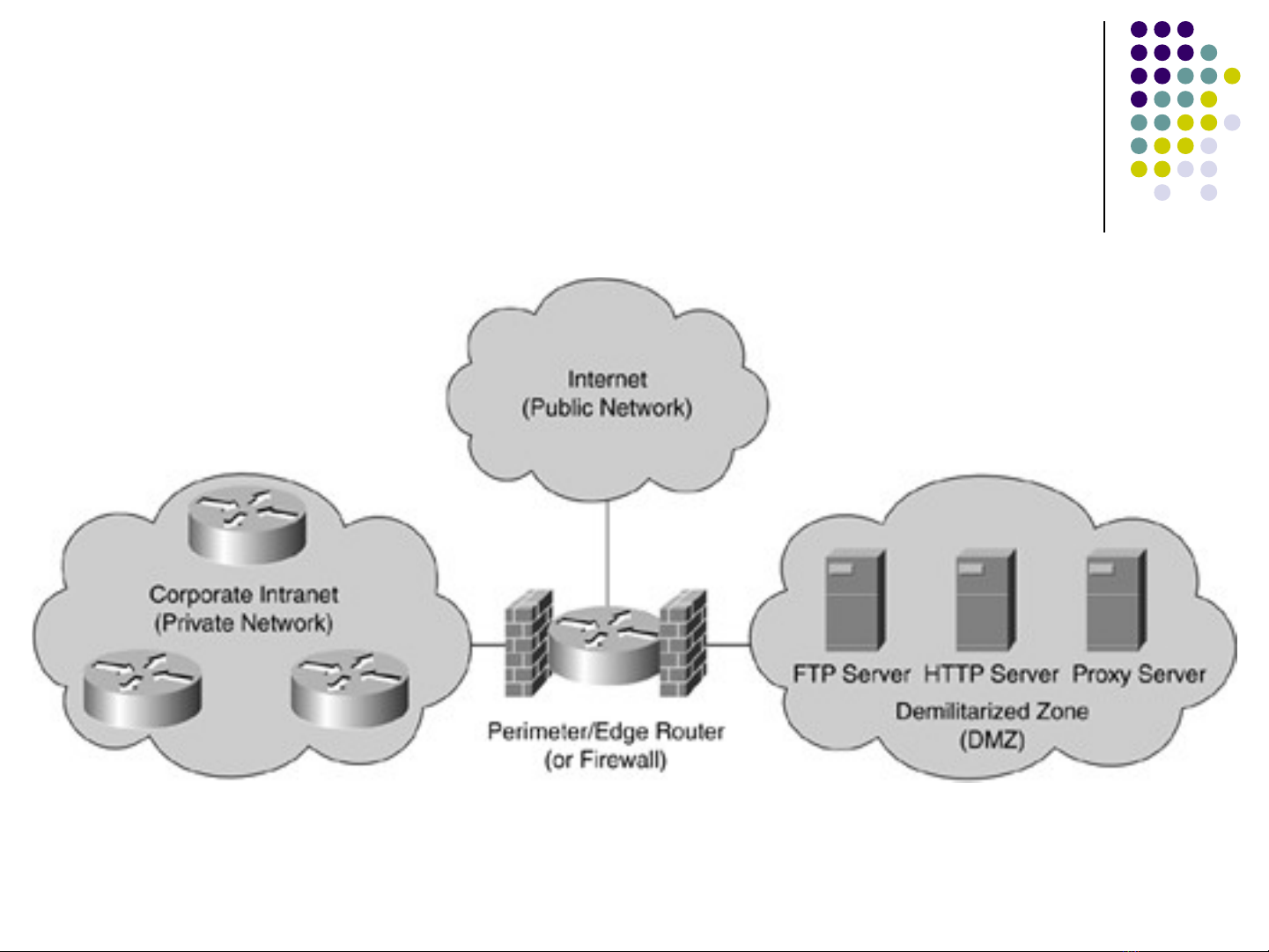
A firewall is defined as a gateway or access
server (hardware- or software-based) or
several gateways or access servers that are
designated as buffers between any
connected public network and a private
network.
A firewall is a device that separates a trusted
network from an untrusted network.
It may be a router, a PC running specialized
software, or a combination of devices.
Các khái ni m c b nệ ơ ả

Các ki u firewall khác nhauể
A multitude of firewall is produced that are capable
of monitoring traffic using different techniques.
Some of firewalls can inspect data packets up to
Layer 4 and others can inspect all layers (deep
packet firewalls).
three types of inspection methodologies
Packet filtering and stateless filtering
Stateful filtering
Deep packet layer inspection



















![Sổ tay Kỹ năng nhận diện & phòng chống lừa đảo trực tuyến [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251017/kimphuong1001/135x160/8271760665726.jpg)
![Cẩm nang An toàn trực tuyến [Mới nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251017/kimphuong1001/135x160/8031760666413.jpg)





