
Facuty of Electronics & Telecommunications, HCMUNS 1
BÀI 4:
MÃ HÓA KÊNH
(Channel coding)
Facuty of Electronics & Telecommunications, HCMUNS
Đặng Lê Khoa
Email:danglekhoa@yahoo.com
dlkhoa@fetel.hcmuns.edu.vn

Facuty of Electronics & Telecommunications, HCMUNS
2006-02-16 Lecture 9 2
Nội dung trình bày
• Mã hóa kênh ( Channel coding )
•Mã hóa khối (Block codes)
+ Mã lập (Repetition Code)
+ Hamming codes
+ Cyclic codes
* Reed-Solomon codes
•Mã hóa chập (Convolutional codes)
+ Encode
+ Decode
Facuty of Electronics & Telecommunications, HCMUNS
2006-02-16 Lecture 9 3
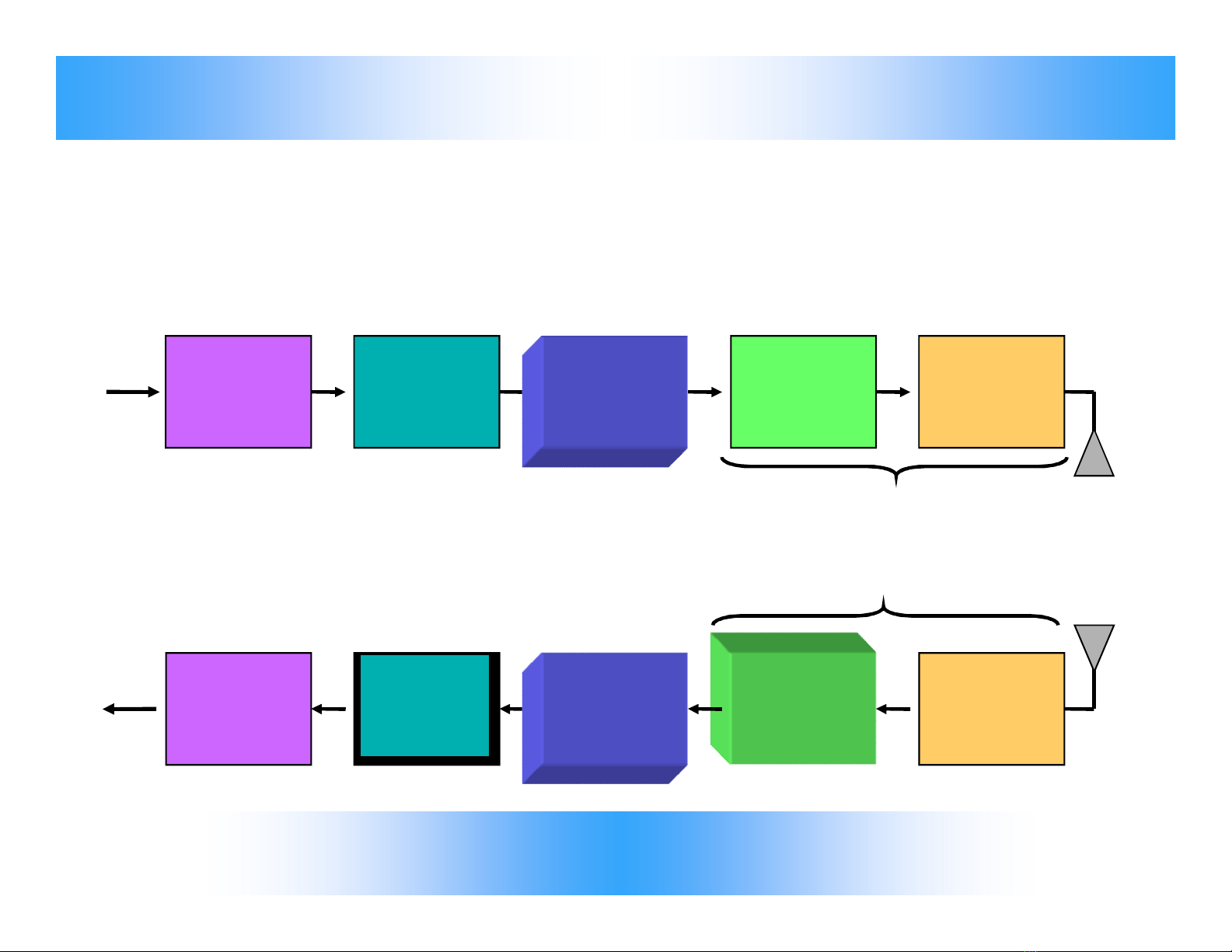
Sơ đồ khối hệ thống DCS
Format Source
encode
Format Source
decode
Channel
encode
Pulse
modulate
Bandpass
modulate
Channel
decode
Demod.
Sample
Detect
Channel
Digital modulation
Digital demodulation

Facuty of Electronics & Telecommunications, HCMUNS
2006-02-16 Lecture 9 4
•Tín hiệu truyền qua kênh truyền sẽ bị ảnh hưởng bởi
nhiễu, can nhiễu, fading… là tín hiệu đầu thu bị sai.
•Mã hóa kênh: dùng để bảo vệ dữ liệu không bị sai
bằng cách thêm vào các bit dư thừa (redundancy).
•Ý tưởng mã hóa kênh là gởi một chuỗi bit có khả
năng sửa lỗi
•Mã hóa kênh không làm giảm lỗi bit truyền mà chỉ làm
giảm lỗi bit dữ liệu (bảng tin)
•Có hai loại mã hóa kênh cơ bản là: Block codes và
Convolutional codes
Channel coding là gì?

Facuty of Electronics & Telecommunications, HCMUNS
2006-02-16 Lecture 9 5
Định lý giới hạn Shannon
•Đối với kênh truyền AWGN, ta có
C: channel capacity (bits per second)
B: transmission bandwidth (Hz)
P: received signal power (watts)
No: single-
sided noise power density (watts/Hz)
Eb: average bit energy
Rb: transmission bit rate
C/B: bandwidth efficiency





















![Bài giảng Nhập môn Kỹ thuật điện [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251208/nguyendoangiabao365@gmail.com/135x160/60591765176011.jpg)




