
Chương 2
Môi trường vi mô internet
ThS. Trần Trí Dũng
26 March 2012
1https://sites.google.com/site/dungtrantri/

Các vấn đề
Các yếu tố môi trường internet ảnh hưởng tới
chiến lược marketing trực tuyến của một tổ
chức
Đánh giá mức độ sử dụng internet của đối thủ
cạnh tranh, khách hàng & trung gian
26 March 2012
2https://sites.google.com/site/dungtrantri/
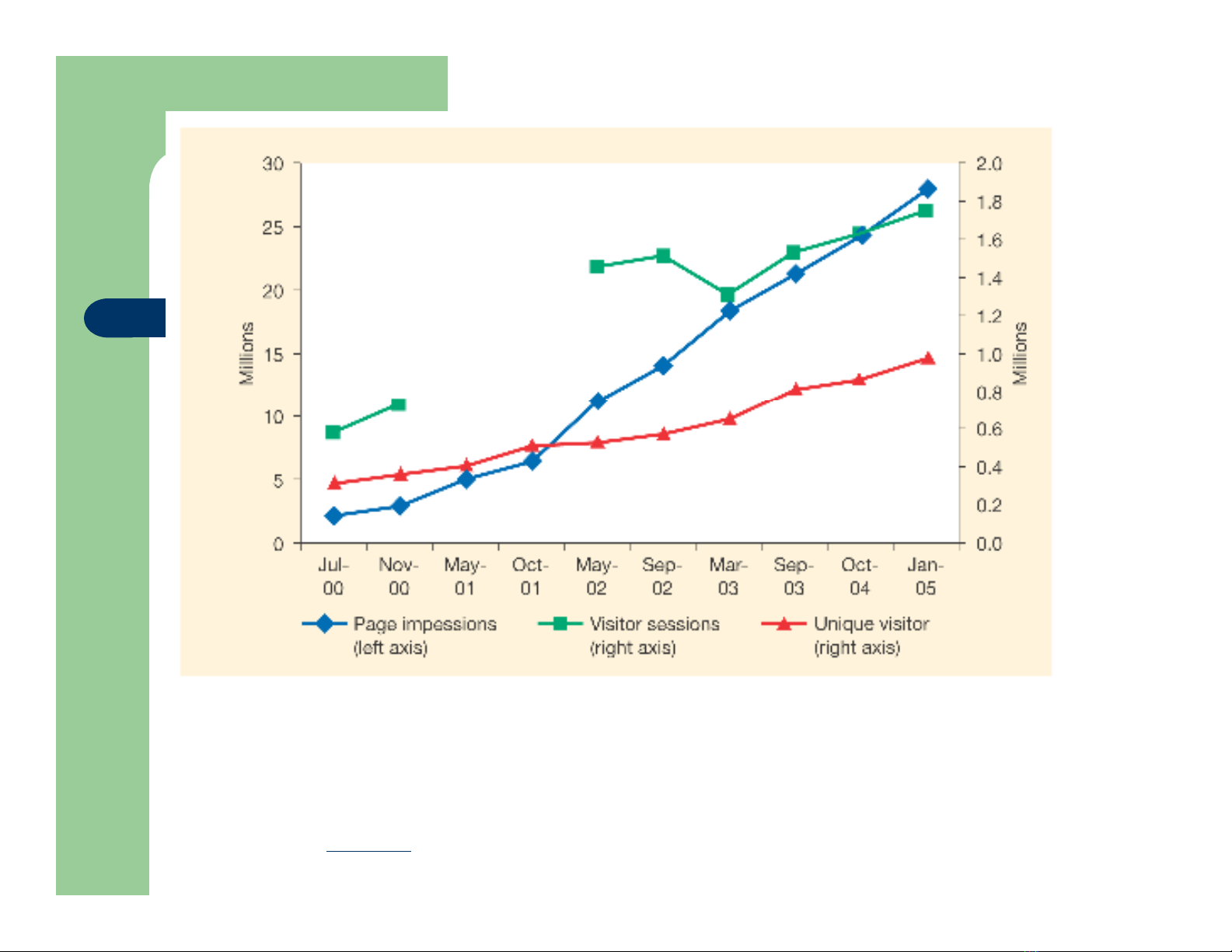
Figure 2.1 Increase in traffic volume at Handbag.com in selected months when
audited. Page impressions are pages served to visitors, visitor sessions are visits
up to a maximum of 30 minutes and unique visitors is the number of individuals
visiting the site in a given month
Source: Compiled from ABC Electronic (ww.abce.org.uk)
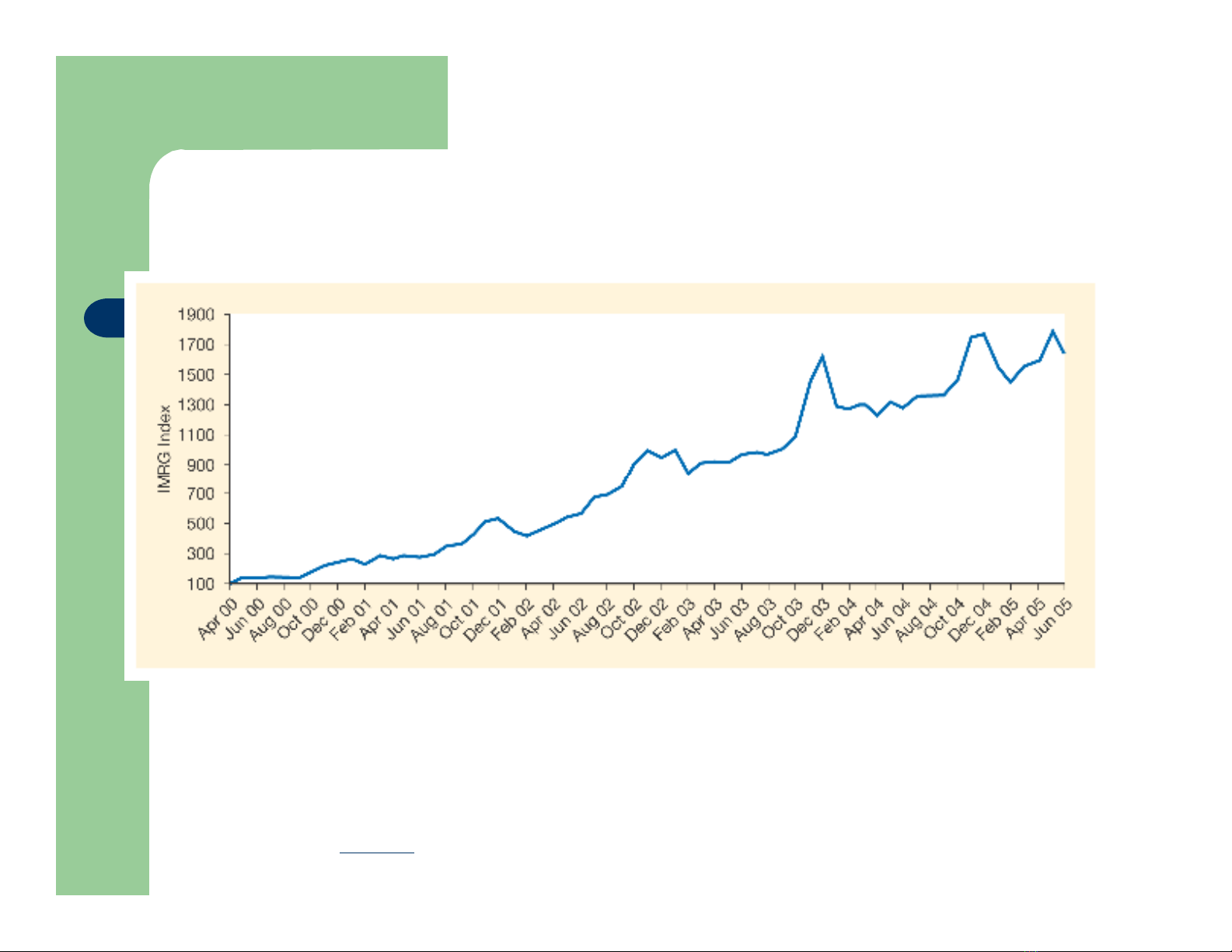
Figure 2.2 The IMRG retail index shows online sales volume in the UK relative to 100
in April 2000
Source: Interactive Media in Retail Group (www.imrg.org)
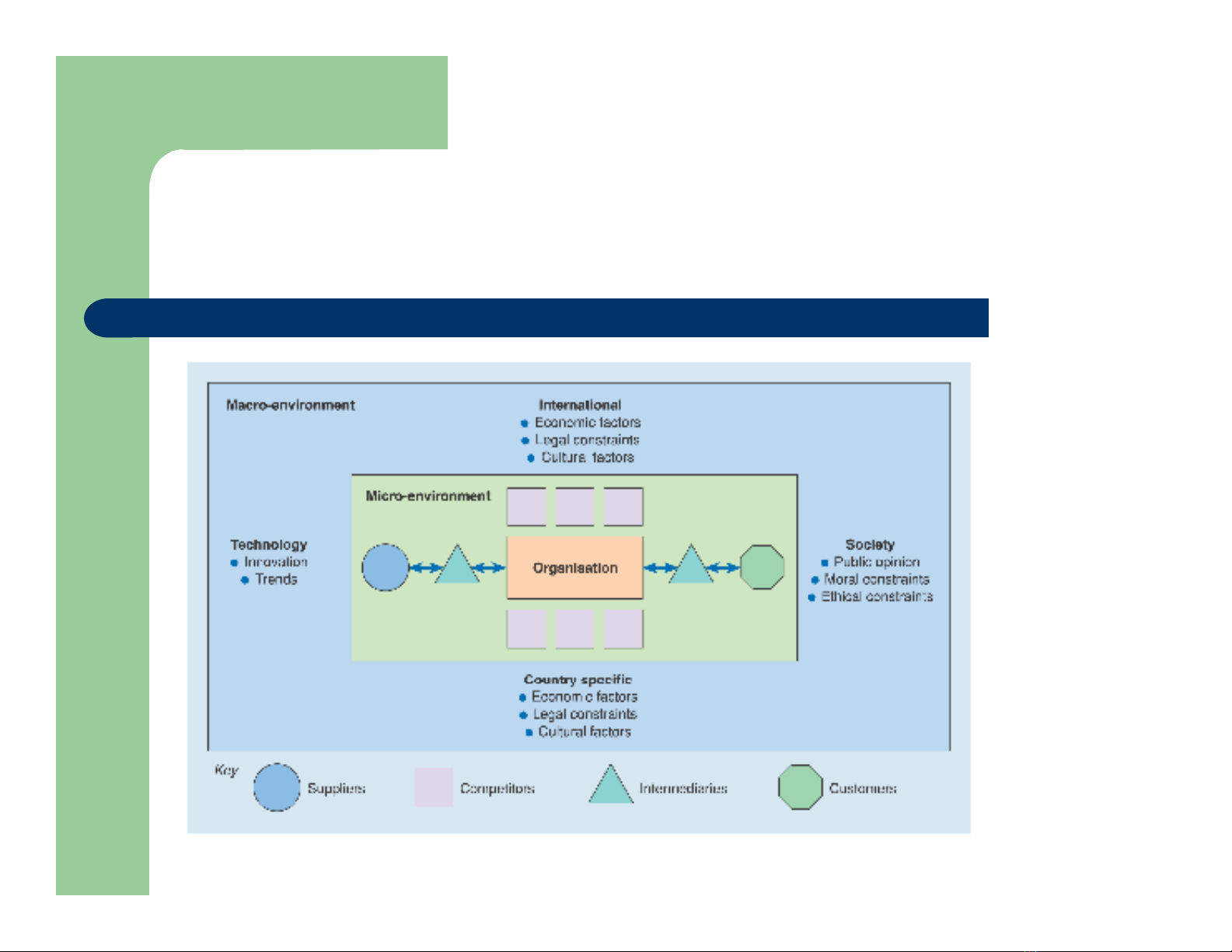
Môi trường marketing internet
26 March 2012 https://sites.google.com/site/dungtrantri/
5
Figure 2.3 The
Internet
marketing
environment


























