
!
!
!"#
$
!
!
"
!
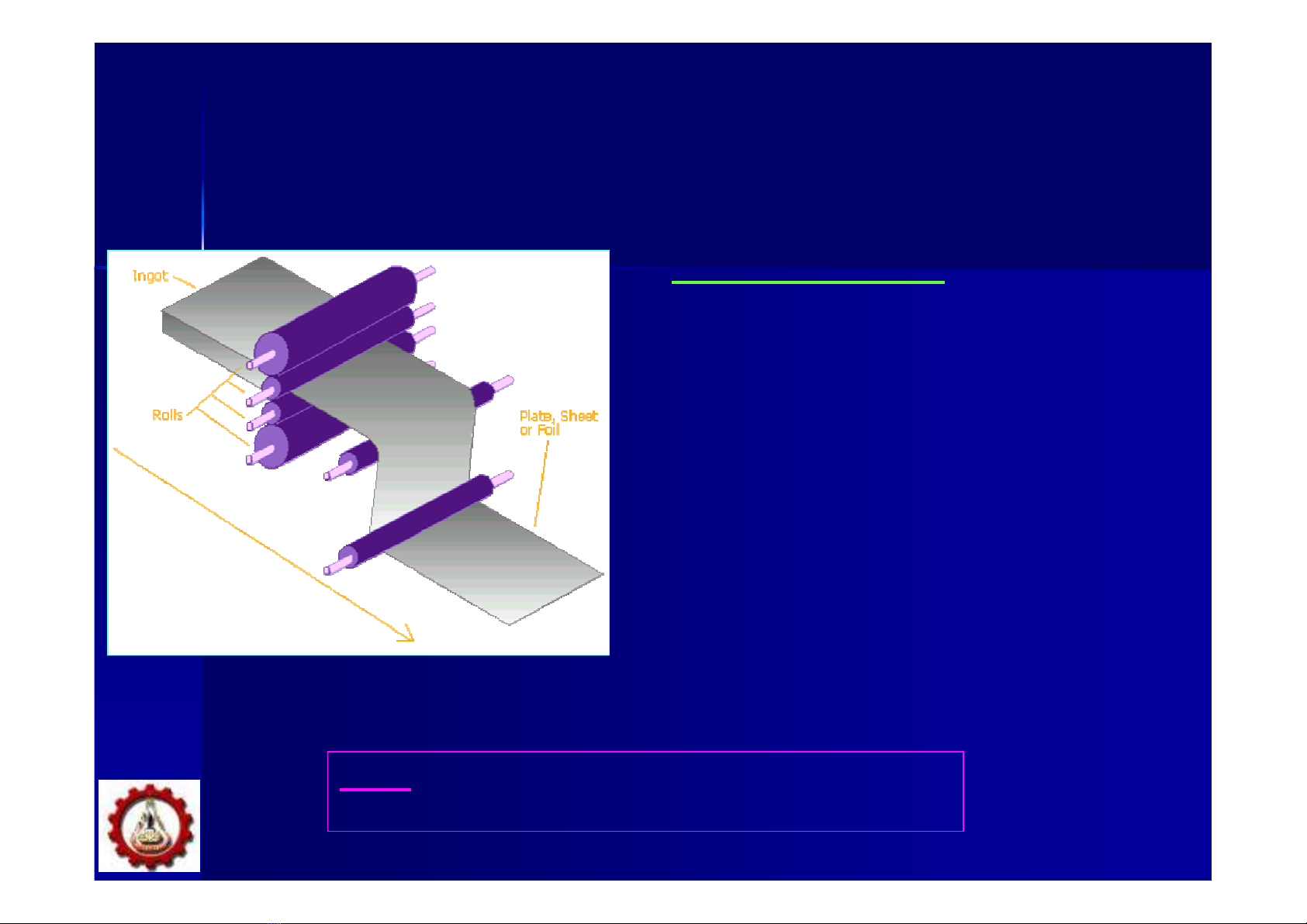
#
!
$
%
!
&
!
###%# %
&'('%

!
%%% %
%!
!
&
%%
!
###%%

$
$













![Bài giảng Ứng dụng tin học trong Kỹ thuật phương tiện thủy [chuẩn nhất]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251216/anhquangvu03@gmail.com/135x160/12021765937860.jpg)





![Bài tập tối ưu trong gia công cắt gọt [kèm lời giải chi tiết]](https://cdn.tailieu.vn/images/document/thumbnail/2025/20251129/dinhd8055/135x160/26351764558606.jpg)





